How to Create a Winning Pricing Strategy + Examples

Are you struggling to set the right price for your products or services? You’re not alone. Your pricing strategy can make or break your business success, affecting everything from your daily sales to your long-term growth.
In this guide, you’ll discover how to choose and implement the right pricing approach for your business, whether you’re launching a new product or looking to optimize your existing pricing structure.
The Importance of Choosing a Suitable Pricing Strategy
Contrary to popular belief, selecting a pricing strategy is not just about setting a number. It actually deeply influences branding, market positioning, and long-term business growth, and is a crucial part of your business plan.
The right approach ensures a balance between customer expectations and business objectives.
Choosing the right pricing strategy can determine your business’s success because it impacts almost every aspect of a business, including revenue, customer perception, and market competitiveness.
A well-thought-out pricing structure helps businesses maximize profitability while staying attractive to their target audience.
Common Pricing Strategies in Marketing
Businesses have multiple approaches to pricing their products and services. Understanding these pricing strategy methods can help you make more informed decisions about how to value your offerings in the marketplace. The right pricing strategy can help you maximize your profits.
Every pricing strategy needs to start with some research into your product, market, and competitors and a good old SWOT analysis to understand your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
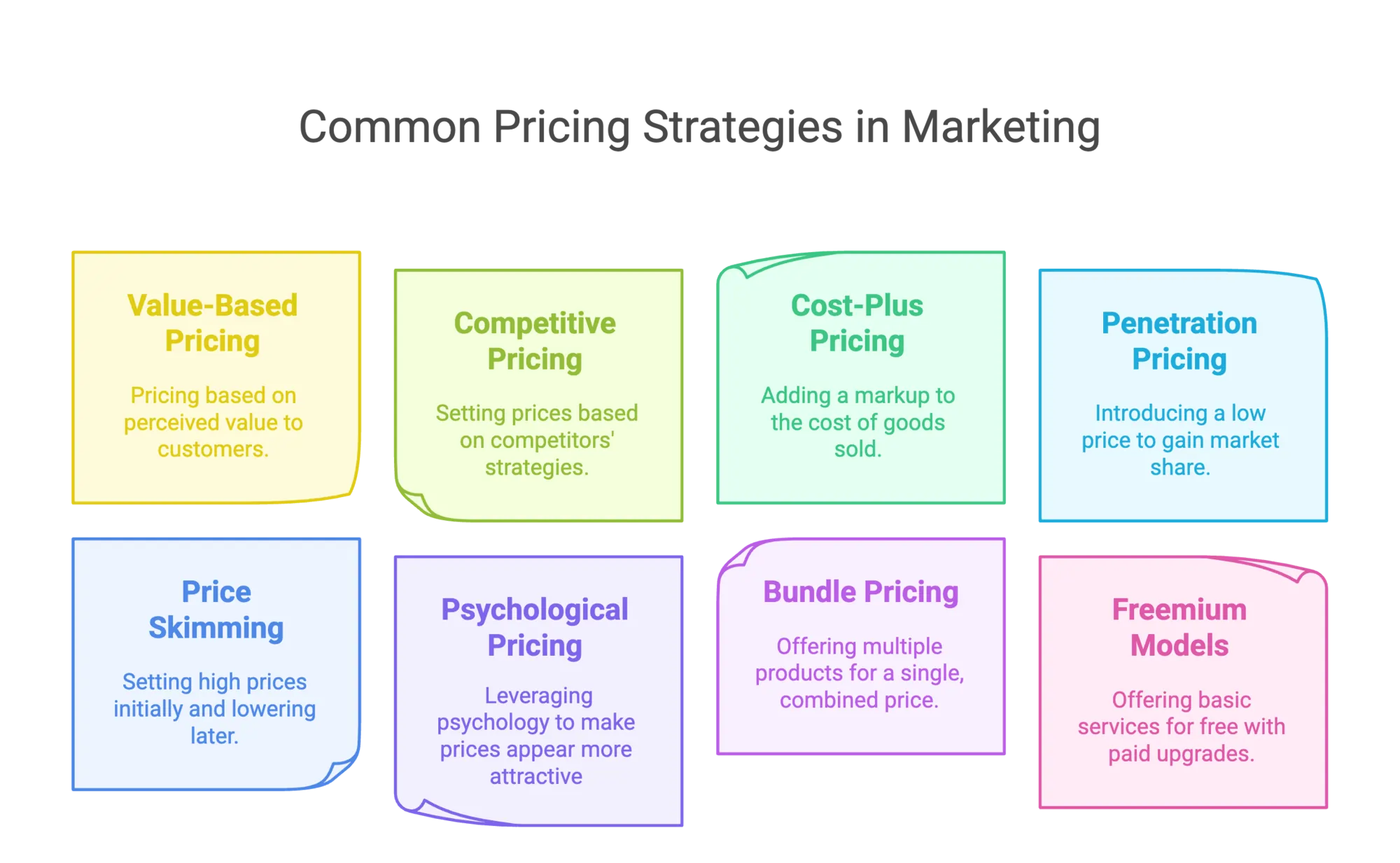
1. Value-Based
Value-based pricing focuses on setting prices according to the perceived worth to customers rather than production costs. This strategy prioritizes customer perception and willingness to pay.
Core Principles:
- Emphasize the product’s unique value
- Price based on customer’s perceived benefit
- Demonstrate exceptional worth beyond basic functionality
Strategic Considerations:
- Requires deep understanding of customer needs
- Demands in-depth market research
- Works best with differentiated products (the process of identifying and communicating the unique qualities of a brand compared to its competitors.)
- Challenges traditional cost-based pricing approaches
2. Competitive Pricing
In this pricing structure, businesses set prices directly in relation to competitors’ rates. The goal is to remain attractive and relevant in the marketplace.
Key Characteristics:
- Continuous market monitoring
- Flexible pricing mechanisms
- Quick adaptation to market changes
- Focus on maintaining market position
Implementation Strategies:
- Regular competitor price tracking
- Dynamic pricing algorithms
- Strategic positioning above or below market rates
- Balancing competitiveness with profitability
3. Cost-Plus Pricing
A straightforward method where businesses calculate total production costs and add a predetermined profit margin to determine the selling price.
Calculation Framework:
- Total Direct Costs (Materials + Labor)
- Indirect Expenses (Utilities + Administrative Costs)
- Overhead Allocation (Fixed Costs + Variable Costs)
- Desired Profit Margin (%)
- Final Selling Price
Formula: Final Selling Price = (Total Direct Costs + Indirect Expenses + Overhead Allocation) × (1 + Profit Margin)
For example, if your total costs are $100 and you want a 25% profit margin: $100 × (1 + 0.25) = $125 Final Selling Price
Advantages:
- Simple to understand and implement
- Ensures cost recovery
- Provides predictable profit margins
- Works well in stable market conditions
4. Penetration Pricing
Companies initially set low prices to attract customers and quickly gain significant market share. As brand loyalty develops, prices gradually increase.
Strategic Approach:
- Initial below-market pricing
- Rapid customer acquisition
- Building brand recognition
- Creating switching barriers for competitors
Potential Risks:
- Potential short-term profitability challenges
- Risk of being perceived as low-quality
- Customer expectations of continued low pricing
- Requires careful long-term planning
5. Price Skimming
This strategy involves launching products at high prices and systematically reducing them over time, targeting different customer segments.
Phased Pricing Methodology:
- Initial high-price point for early adopters
- Gradual price reductions
- Segmented market penetration
- Maximizing revenue across product lifecycle
Psychological Dynamics:
- Creates the perception of exclusivity
- Attracts innovation-seeking customers
- Manages product demand curve
6. Psychological Pricing
This is all about leveraging consumer psychology to make prices appear more attractive and influence purchasing decisions.
Pricing Techniques:
- Charm pricing: Ending prices in .99 dollars
- Comparison pricing: Comparing the price of a similar product from different brands.
- Decoy pricing: Businesses introduce a third product option that is purposefully less attractive.
- Prestige pricing: Prices are purposely set high for branding needs.
Cognitive Triggers:
- Perception of better value
- Emotional purchasing decisions
- Reduction of price sensitivity
- Creating the illusion of savings
7. Bundle Pricing
Packaging multiple products or services at a reduced combined rate to increase perceived value and encourage higher purchase volumes.
Bundling Strategies:
- Pure bundling
- Mixed bundling
- Complementary product combinations
- Volume-based discounts
Business insight: With pure bundling, customers can only purchase items as a complete package. Mixed bundling gives customers the choice to buy either the full package or any of its individual items separately.
Strategic Benefits:
- Increased average transaction value
- Reduced customer decision complexity
- Enhanced product visibility
- Inventory management optimization
8. Freemium/Subscription Models
Offering basic features for free while charging for advanced functionalities, creating a low-barrier entry point with upselling opportunities.
Model Characteristics:
- Free base-level service
- Premium feature access
- Tiered pricing structures
- Continuous value demonstration
Conversion Mechanics:
- Low-risk customer acquisition
- Gradual value revelation
- User experience-driven upgrades
- Predictable recurring revenue
Each offers unique advantages and challenges. The most effective approach depends on your specific business model, market dynamics, and customer expectations.
Real-World Pricing Examples
So you’re probably wondering, how do companies formulate a pricing strategy? Let’s take a look at some pricing strategy examples.
1. Zapier’s Strategic Pricing Model Approach
Zapier pioneered a multi-tiered approach in the SaaS world. The Zapier AI workflow automation platform offers a freemium tier and a subscription model. It’s pricing strategy breaks down like this:
Free Tier:
- Basic automation capabilities
- Limited monthly task volume
- Attracts small businesses and individuals
- Serves as an entry point for potential upgrades
Paid Tiers:
- Progressively unlock more advanced features
- Increase task automation limits
- Provide premium integrations
- Cater to growing business needs
By offering scalable options, Zapier creates a frictionless path from casual user to committed customer. Their model demonstrates how flexible pricing can drive user acquisition and retention.
2. Adobe’s Subscription Revolution
Adobe completely transformed its pricing structure by shifting from:
- Traditional one-time software purchases
- Expensive perpetual licenses
- Limited update access
To:
- Monthly/annual cloud subscriptions
- Continuous software updates
- Lower upfront costs
- Seamless access across devices
This approach made professional creative tools more accessible to freelancers, students, and small businesses while creating predictable recurring revenue.
It also allows customers to choose the tools they need for their business, be it Adobe Dreamweaver for web design or Adobe Photoshop for graphic design.
3. Amazon Prime: The Ultimate Bundle Pricing Strategy
Amazon Prime represents a masterclass in bundle pricing:
What’s Included:
- Free two-day shipping
- Video streaming platform
- Music streaming service
- Cloud storage
- Gaming benefits
- Additional retail perks
Pricing Psychology:
- Single affordable monthly fee
- Creates perceived massive value
- Encourages increased platform engagement
- Reduces customer price sensitivity
Each service individually might seem expensive, but bundled together, they create irresistible perceived value. This approach transforms a simple shipping subscription into a comprehensive lifestyle service.
Key Takeaways
These examples showcase how innovative pricing strategies in marketing can:
- Lower customer acquisition barriers
- Create flexible value propositions
- Generate predictable revenue
- Adapt to changing market dynamics
The most successful pricing strategies aren’t just about numbers—they’re about understanding and serving customer needs.
Pros and Cons of Different Pricing Strategies
Choosing the right pricing strategy depends on various factors, including business goals, industry dynamics, and customer behavior.
|
Pricing Strategy |
Pros |
Cons |
|
Value-Based Pricing |
|
|
|
Competitive Pricing |
|
|
|
Cost-Plus Pricing |
|
|
|
Penetration Pricing |
|
|
|
Price Skimming |
|
|
|
Psychological Pricing |
|
|
|
Bundle Pricing |
|
|
|
Freemium/ Subscription |
|
|
Factors That Determine a Pricing Strategy
Your ideal pricing approach depends on several key elements:
- Your target market – Understanding who your customers are and what they can afford helps you set appropriate prices.
- Economic market conditions – conditions, competition, and industry trends all affect pricing decisions.
- Production costs – You need to cover your expenses while maintaining healthy margins.
- Brand positioning – Your prices should reflect how you want customers to perceive your brand.
- Business goals – Different goals (market share, profit maximization, growth) require different pricing approaches.
How to Select the Right Pricing Strategy for Your Business
Selecting the right pricing strategy involves assessing various factors, including your target market, competition, costs, and business objectives.
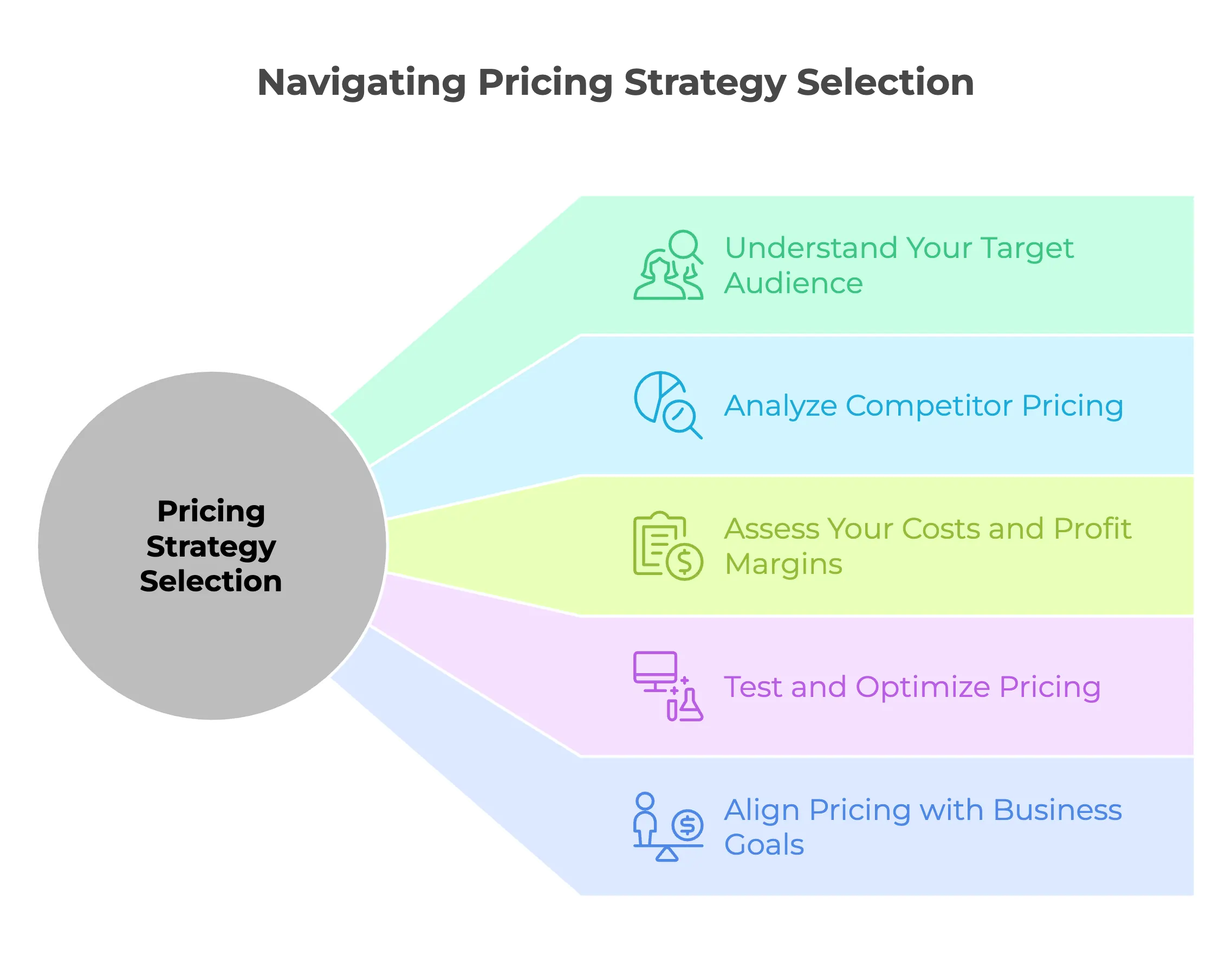
Here are five key steps to help determine the best pricing model for your business:
1. Understand Your Target Audience
Conduct market research to understand your customers’ willingness to pay, preferences, and perceived value of your product. Segmenting your audience based on demographics, purchasing behavior, and income levels will provide insights into the pricing structure that best resonates with them.
You can:
- Run customer surveys to learn what they value most
- Look at their buying habits and patterns
- Consider their budget ranges and price sensitivity
- Ask for customer feedback on the current pricing
2. Analyze Competitor Pricing
Research your competitors’ pricing strategies to identify market trends and potential gaps. Competitive analysis helps determine whether you should adopt a premium, budget-friendly, or differentiated pricing approach to stand out.
Your competition can teach you a lot about pricing in your market:
- Track their regular prices and special offers
- Notice how they position different product tiers
- Look for gaps where you can offer better value
- Consider how you can differentiate your pricing
3. Assess Your Costs and Profit Margins
Calculate production, operational, and marketing costs to ensure your pricing strategy maintains profitability. Factor in both fixed and variable costs to set a price that covers expenses while achieving revenue goals.
Before setting prices, make sure you understand your costs:
- Calculate all production expenses
- Include overhead costs like rent and utilities
- Factor in marketing and sales expenses
- Set target profit margins for each product
4. Test and Optimize Pricing
Consider A/B testing different pricing strategies to gauge customer responses and adjust accordingly. Regularly review pricing performance metrics to refine your approach based on market conditions and consumer behavior.
Don’t be afraid to experiment with your pricing:
- Try different price points with similar customer groups
- Test various discount strategies
- Monitor how sales volume changes with price adjustments
- Collect customer feedback about price changes
5. Align Pricing with Business Goals
Ensure your pricing strategy aligns with long-term business objectives, whether it’s maximizing short-term profits, increasing market share, or building brand loyalty. Flexibility is key to adapting to industry changes and sustaining growth.
Your pricing strategy needs to support your business goals:
- Consider your brand positioning
- Plan for future growth and expansion
- Build in room for seasonal adjustments
- Keep some flexibility for market changes
Remember, you can adjust your strategy as you learn what works best. Start with small changes and measure their impact before making bigger adjustments. The key is finding a balance between what your customers will pay and what helps your business grow.
How AI Tools Can Help You Create a Winning Pricing Strategy
AI tools for research like ChatGPT, Claude AI, and Gemini AI can help you analyze pricing strategies by processing large amounts of data, identifying trends, and offering insights tailored to your business. They assist in competitor analysis, pricing model optimization, and predicting customer responses, ensuring your pricing remains competitive and profitable.
ChatGPT: Need quick pricing suggestions or competitor analysis? ChatGPT can generate ideas based on industry trends, customer preferences, and pricing models. It helps you brainstorm new pricing strategies efficiently.
Claude AI: If you need in-depth analysis, Claude AI can process complex datasets and suggest optimized pricing structures. It’s great for evaluating customer behavior, pricing elasticity, and market positioning.
Gemini AI: Google’s Gemini AI leverages real-time search data and economic trends to predict how price changes might impact your sales. It can also help forecast demand and fine-tune dynamic pricing strategies.
By using AI-powered tools, you can develop a pricing strategy that aligns with market conditions, maximizes revenue, and stays competitive.
Example: ChatGPT for research
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right pricing strategy is essential for business success. By understanding market dynamics, customer behavior, and competitive positioning, businesses can develop a pricing model that maximizes profitability while ensuring long-term sustainability.
The key is finding the right balance—one that keeps customers happy while supporting your bottom line.
Don’t be afraid to test different strategies and adjust as needed. Pricing isn’t just about numbers — it’s about delivering value and staying competitive. Keep learning, stay flexible, and refine your approach over time. With the right pricing strategy, your business can thrive in any market.
FAQ
Q: Can you combine pricing strategies?
A: Yes, businesses often combine different pricing strategies to optimize revenue and market appeal. For example, a company may use value-based pricing for premium products while adopting penetration pricing for new market entries.
Q: What are the 5 C’s of pricing?
A: The 5 C’s of pricing are Cost, Customers, Competition, Channel, and Company objectives. These factors help determine the most effective pricing strategy.
Q: How do pricing models work?
A: Pricing models define how businesses charge for their products or services. They can be based on costs, perceived value, market demand, or competitive benchmarks.
Q: How to pick a pricing model?
A: Selecting a pricing model requires analyzing costs, customer demand, competitor pricing, and overall business goals.
Q: What is the formula for pricing?
A: A common formula is: Selling Price = Cost Price + Markup Percentage
Q: How to find CP?
A: CP (Cost Price) is determined by calculating all production and operational costs associated with a product or service.




