How to Write a Business Plan To Fund Your Business

Starting a business can be both exciting and overwhelming, especially when it comes to creating a business plan. But don’t worry, we’ve got you covered! This guide will walk you through the process step by step, making it easier to turn your ideas into a clear, actionable plan. Whether you’re seeking funding or just want to map out your strategy, this guide will walk you through so you can confidently get there.
TL;DR – Simple Guide to Writing a Business Plan
This step-by-step guide shows you how to write a clear, effective business plan. Perfect for startups and small businesses seeking funding or growth.
- Define your mission, goals, and value proposition
- Conduct in-depth market research and competitive analysis
- Structure your business operations and management team
- Develop marketing, sales, and go-to-market strategies
- Create clear financial projections and funding plans
- Avoid common mistakes like vague goals or unrealistic forecasts
Plus, you’ll get tips, templates, and AI tools to streamline your planning process. By the end, you’ll have a professional business plan that sets your company up for long-term success.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a company’s goals, the strategy and timeline to achieve them, and the financial needs to support these objectives. It serves as a roadmap for business operations, helping to clarify the business idea, market potential, and strategic direction.
Business Plan Outline
A business plan communicates the company’s vision and mission, detailing its products or services, market analysis, competitive edge, and financial forecasts. It is essential for securing funding from investors or lenders, guiding business operations, and measuring success.
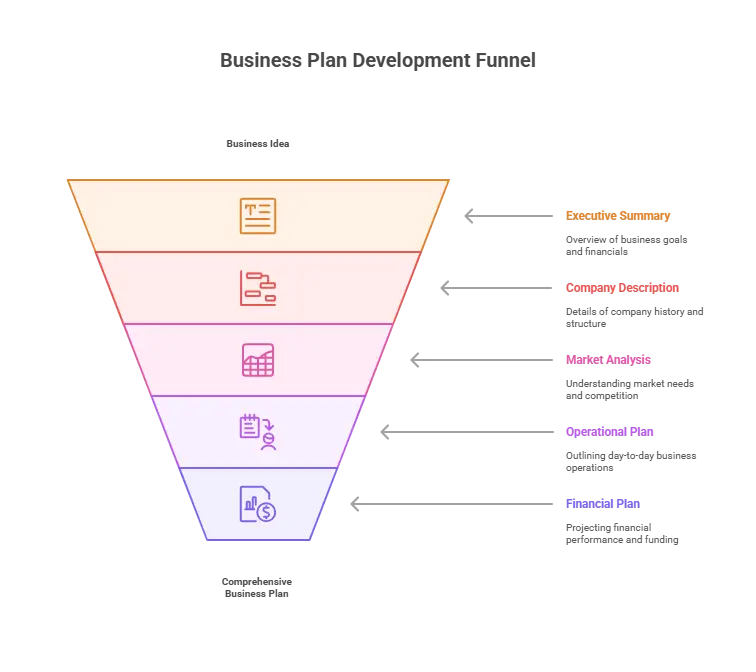
1. The Executive Summary Section
- Mission Statement: Briefly describe the purpose of the business and what it aims to achieve.
- Company Overview: Provide a summary of what your company does, its target market, and what makes it unique.
- Business Objectives: Outline the short-term and long-term goals of the business.
- Financial Highlights: Summarize the expected revenue, profit margins, and key financial metrics.
- Funding Requirements: State how much funding is needed and briefly describe how it will be used.
2. The Company Description Section
- Company History: Provide a brief company history, including key milestones.
- Business Structure: Explain the business’s legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation).
- Ownership and Management: Outline the ownership structure and introduce the management team.
- Location and Facilities: Describe the business’s location, facilities, and key assets.
3. Market Research and Analysis
- Industry Overview: Provide an industry overview, including trends, growth projections, and key success factors.
- Target Market: Define the target market, including demographics, psychographics, and geographic location.
- Market Needs: Identify the key needs and problems your business will solve for the target market.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze the competition, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses and how your business will differentiate itself.
4. Organization and Management
- Organizational Structure: Describe the company’s organizational structure, including roles and responsibilities.
- Management Team: Introduce the management team, their qualifications, and relevant experience.
- Advisory Board: If applicable, list any advisory board members and their contributions to the business.
5. Products or Services
- Product/Service Description: Describe the products or services your business will offer.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Explain what makes your product or service unique and how it meets the target market’s needs.
- Product Lifecycle: Outline the lifecycle of your product or service, including development, growth, maturity, and decline stages.
- Research and Development: Describe any ongoing or future research and development activities.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Marketing Strategy: Outline the marketing strategies you will use to reach your target market, including branding, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
- Sales Strategy: Describe your sales process, tactics, and team structure.
- Customer Acquisition: Explain how you will attract and retain customers.
- Partnerships and Alliances: List any partnerships or alliances to help you achieve your business goals.
7. Operational Plan
- Operations Overview: Describe the day-to-day operations of the business, including production, inventory management, and quality control.
- Suppliers and Vendors: List key suppliers and vendors and explain how you will manage supply chain relationships.
- Technology and Equipment: Detail the technology and equipment necessary for operations.
- Milestones and Metrics: Outline key milestones and performance metrics to track the business’s progress.
8. Financial Plan
- Revenue Model: Explain how the business will generate revenue, including pricing strategy and revenue streams.
- Financial Projections: Provide detailed financial projections, including income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets for the next 3-5 years.
- Break-Even Analysis: Calculate the break-even point and explain when the business is expected to become profitable.
- Funding Requirements: Detail the amount needed, how it will be used, and the expected return on investment (ROI).
- Exit Strategy: Outline potential exit strategies for investors, such as acquisition, IPO, or buyout.
9. Appendices
- Resumes of Key Team Members: Include the resumes of the management team and key personnel.
- Market Research Data: Provide detailed market research and data that support your business plan.
- Product/Service Documentation: Include any additional documentation about your products or services, such as technical specifications, patents, or prototypes.
- Legal Documents: Attach any relevant documents, such as business licenses, contracts, or agreements.
- Additional Financial Documents: Provide any additional financial documents, such as tax returns, credit reports, or letters of intent from potential customers.
How to Write a Successful Business Plan Step-by-Step
Now that you’ve seen the overall outline, let’s dive deeper into each section and explore what to include, how to write it, and real-world tips.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary provides an overview of your business, its mission, and its objectives. This section should be concise and engaging. This should be seen as your elevator pitch — it is the first thing your potential investors will read. Here’s what you’ll need to include:
- Business concept
- Business goals and vision
- Product or service description
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- The ask (funding request, if applicable)

2. Company Description
This section explains what your company does, its mission statement, and its unique value proposition more in-depth and comprehensively than the executive summary. Include:
- Business name and location
- The nature of the business and the market needs it addresses
- Competitive advantage
- Vision and mission
- Brief history and current status
- Future goals and objectives
3. Market Analysis
Market analysis demonstrates your knowledge of the industry and market. It should include:
- Industry description and outlook
- Key market research, statistics, and trends
- Market size and growth potential
- Target market needs
- Regulatory environment and barriers to entry
Target Market Identification:
Identify the specific segment of the market your business will target. This involves:
- Demographic details: Age, gender, income, education.
- Geographic details: location, urban/rural
- Psychographic details: lifestyle, values, interests
- Behavioral details: buying habits, brand loyalty
Customer Segmentation:
Break down your target market into specific customer segments. Each segment should be:
- Clearly defined and distinct
- Measurable in size and purchasing power
- Accessible through your marketing efforts
- Substantial enough to be profitable
Competitive Analysis:
Understanding your competitors is crucial. This section should include:
- Direct competitors: Businesses offering similar products or services
- Indirect competitors: Businesses offering alternative solutions
- Competitive advantage: What sets your business apart
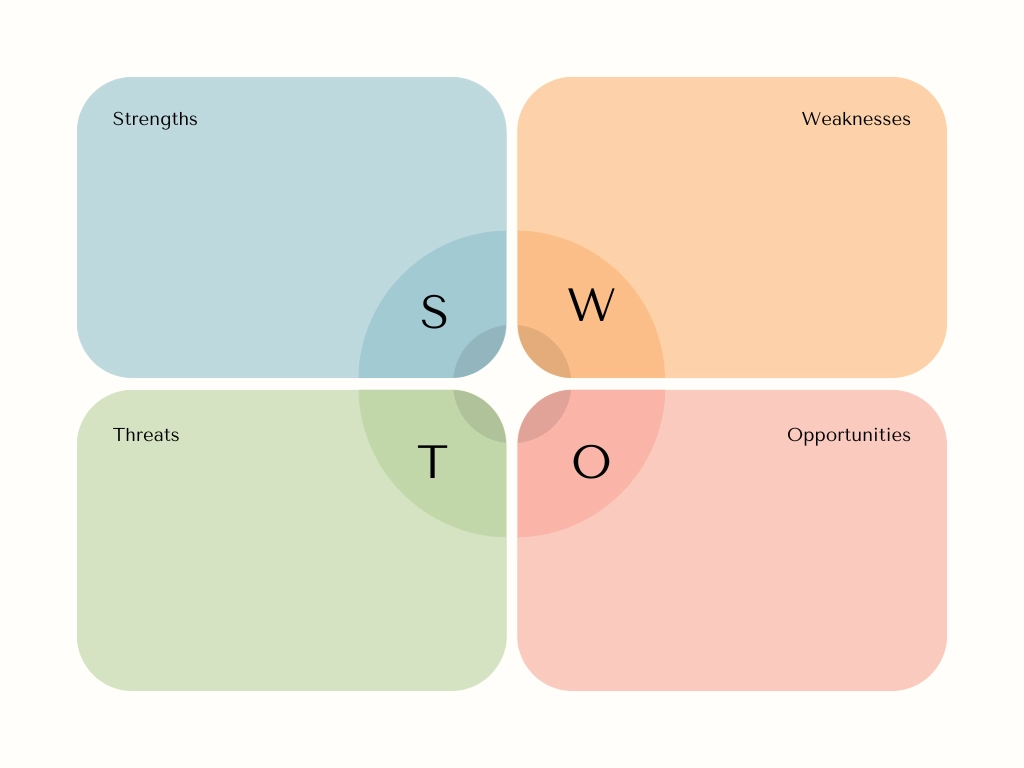
- SWOT analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
4. Organizational Structure and Management
Detail the structure of your business and the team behind it. Include:
- Organizational chart with defined roles & responsibilities
- Ownership structure: sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation
- Key management roles and responsibilities
- Backgrounds and qualifications of key team members
5. Products and Services
Describe the products or services your business offers. This section should cover:
- Detailed description of products/services
- Unique features and benefits
- Lifecycle stage: development, growth, maturity
- Research and development activities
- Future products or services pipeline
6. Marketing & Sales
Outline your marketing & sales strategy, focusing on how you plan to attract and retain customers. Include:
- Market positioning and branding strategy
- Pricing strategy
- Distribution channels
- Promotional strategy: Advertising, sales promotions, public relations.
- Digital marketing tactics: Social media, email marketing, content marketing.
- Sales goals and targets
- Sales tactics: direct sales, online sales, partnerships
- Sales cycle: steps from lead generation to closing
- Customer relationship management
- Sales team structure and compensation
7. Funding Request
If you are seeking funding, this section should outline your needs clearly. Include:
- Amount of funding needed
- Intended use of funds: working capital, equipment, marketing
- Future funding requirements
- Strategic financial plans for growth
8. Financial Projections
Provide detailed financial forecasts that demonstrate the potential profitability of your business. Include:
Income Statement:
Projects revenue, costs, and profits over a period (usually three to five years). Key components are:
- Revenue projections
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Gross profit margin
- Operating expenses
- Net profit
Cash Flow Statement:
Shows the flow of cash in and out of your business. The key components are:
- Operating activities: cash generated from business operations
- Investing activities: cash used for investments in the business
- Financing activities: cash from loans, investments, or dividends

Balance Sheet
Provides a snapshot of your business’s financial position at a given time.
The key components are:
- Assets: current and non-current
- Liabilities: current and long-term
- Equity: owner’s equity, retained earnings
If you’re a startup or young business, you may not have that much financial information yet. That said, every other company will be expected to include income or profit-loss statements, a balance sheet, a cash flow statement, and more relevant financial reports.
If you have existing accounting software, you should easily access these statements. Additionally, it should assist you in calculating the metrics stated above.
Writing a comprehensive business plan is essential for guiding your business strategy, securing funding, and ensuring long-term success. Following these step-by-step instructions, you can create a robust business plan that effectively communicates your vision and plans to stakeholders and investors.
Download Free Templates for Business Plans
Having a well-structured template can significantly simplify creating a business plan. Here are two free templates to help you get started. Be sure to tailor each section to reflect your business’s unique aspects and needs to create a compelling and actionable plan:
Traditional Business Plan Template
Why Write a Business Plan?
Creating a business plan is crucial for startups, small businesses & established businesses. For startups, it provides a structured approach to turning an idea into a viable business. For established businesses, a business plan aids in strategic planning and managing growth.
Benefits of a Business Plan
- Securing funding: Essential for attracting investors or obtaining loans.
- Strategic direction: Provides a clear roadmap and strategic focus.
- Performance measurement or KPIs: Helps track progress against set objectives.
- Risk management: Identifies potential challenges and outlines mitigation strategies.
- Resource allocation: Ensures efficient use of resources by prioritizing key activities.
- Communication tool: Communicates the business vision and strategy to relevant stakeholders.
Creating a business plan is not just a formality but a critical tool for business success and sustainability.
Tips for Creating a Successful Business Plan
Here are some crucial tips to ensure you know how to build a business plan and to ensure it is comprehensive, clear, and effective:
- Market Analysis
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- Growth Strategy
- Business Focus and Clarity
- SWOT Analysis
- KPIs and Performance Metrics
- Go-to-Market Strategy
Market Analysis
Understanding your market is critical to your business’s success. Conduct thorough research to determine the market size, growth potential, and trends. Analyze your target audience’s demographics, behaviors, and needs.
For example, if you’re launching a tech gadget, assess the tech adoption rate and purchasing power in your target demographics. Use reliable sources such as industry reports, market surveys, and competitor analysis to gather data. Here are the practical steps you should take:
- Define Your Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with your market research, which includes understanding consumer demand, assessing market size, and identifying competitors.
- Identify Your Target Audience: Determine who your potential customers are. Create detailed buyer personas that include demographics, psychographics, and behaviors.
- Conduct research: Select a combination of industry reports, such as IBISWorld or Statista, governmental publications, academic research, and competitor analysis tools that will provide comprehensive data.
- Collect data: Gather data systematically using the chosen methods. Ensure your sample size is large enough to provide reliable insights.
- Analyze data: Interpret the data using data analysis techniques. These could include a SWOT analysis, a PEST analysis, customer segmentation, or Porter’s Five Forces. Look for patterns, trends, and insights to inform your business strategy.
- Present findings: Compile your findings into a clear and actionable report. Include visual aids like charts and graphs to illustrate key points.
- Implement insights: Use the insights gained from your market research to inform your business decisions. This could involve adjusting your marketing strategy, refining your product offerings, or exploring new market opportunities.
By following these steps and utilizing these techniques, you can conduct effective market research to provide a solid foundation for your business plan and strategy.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Your USP differentiates your business from competitors. Clearly define what makes your product or service unique and why customers should choose you over others. For instance, if you’re in the food delivery business, your USP could be offering organic meals with delivery in under 30 minutes. To determine your USP, you must take the following steps:
- Identify Customer Pain Points: Understand your target audience’s specific needs and problems.
- Highlight Unique Features: Focus on what makes your product or service different and better than the competition.
- Communicate Value: Clearly articulate the benefits and value customers will receive from your product or service.
Growth Strategy (including Quick Growth Opportunities)
Identify both short-term and long-term growth opportunities. Quick growth can be achieved by targeting underserved market segments, leveraging new technologies, or forming strategic partnerships.
For example, a fashion retailer might quickly grow by collaborating with popular influencers. Consider expanding your product lines, entering new geographical markets, or developing new business models for long-term growth. A better understanding of best practices for business growth is crucial so you know what you need to prioritize to reach your goals.
Business Focus and Clarity
Maintain a clear and focused approach to your business plan. Every section should be concise and to the point, avoiding jargon and overly technical language. Clearly outline your business objectives and ensure all stakeholders understand your vision and goals.
For example, a startup might set a clear goal to become a market leader in eco-friendly packaging within five years.
SWOT Analysis
Conducting a SWOT analysis and competitor analysis is crucial for identifying your business’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats and understanding your competitive landscape.
This helps you craft a compelling, unique selling proposition (USP) and develop effective strategies. Here’s how to do it:
Identifying Direct and Indirect Competitors
Direct Competitors:
- Definition: Direct competitors are businesses offering the same or similar products or services as your business, targeting the same customer base.
- Identification: Look at companies within your industry that serve the same market. For example, if you are launching a new coffee shop, direct competitors are other coffee shops in your area.
- Research Methods: Visit their websites, read customer reviews, visit their physical locations, and analyze their marketing materials.
Indirect Competitors:
- Definition: Indirect competitors offer different products or services that satisfy the same customer need or solve the same problem.
- Identification: Consider businesses that offer alternative solutions. For example, a coffee shop’s indirect competitors could be juice bars or cafes offering a different type of experience.
- Research Methods: Like direct competitors, analyze their online presence, customer feedback, and market strategies.
Assessing Competitors’ Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths:
- Quality of Products/Services: Evaluate the quality and variety of competitors’ offerings.
- Customer Base: Look at their market reach and customer loyalty.
- Brand Reputation: Assess their brand image and reputation in the market.
- Marketing Strategy: Analyze their marketing campaigns, online presence, and advertising methods.
Weaknesses:
- Customer Complaints: Identify common complaints or negative reviews.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Look for any visible operational challenges.
- Product/Service Gaps: Notice areas where their offerings may be lacking or could be improved.
KPIs and Performance Metrics
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your business. KPIs could include metrics like customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, profit margins, and sales growth rates.
For instan
Go-to-Market Strategy
Develop a comprehensive go-to-market strategy that outlines how you will reach your target customers and achieve a competitive advantage. This should include:
- Market Positioning: How you want your brand to be perceived in the market. For example, positioning a premium coffee brand as the go-to choice for coffee connoisseurs.
- Pricing Strategy: Competitive pricing models that reflect the value of your products. For instance, you could use a penetration pricing strategy to gain market share quickly.
- Distribution Channels: The platforms and locations where customers can purchase your products, such as online stores, retail partnerships, or direct sales.
- Promotional Tactics: Marketing activities like advertising, social media campaigns, sales promotions, and public relations efforts. For example, launching a social media campaign targeting health-conscious consumers for a new line of fitness products.
By incorporating these tips and examples into your business plan, you can create a robust and effective roadmap that will guide your business to success.
Types of Business Plans
Different types of business plans cater to specific purposes and audiences, depending on your business goals, stage, and target market. Here are the main types:
- Traditional business plans: Comprehensive documents used to secure funding, including sections like market analysis, organizational structure, and financial projections. Ideal for businesses seeking detailed planning and investment.
- Example: A manufacturing company seeking substantial investment would use a traditional plan to present a thorough market analysis and growth strategy.
- Lean business plans: Concise plans focused on key business aspects designed for internal use to maintain flexibility and adapt quickly to market changes.
- Example: A tech startup using agile methods might use a lean plan to highlight its value proposition and target market.
- Nonprofit business plans: Emphasize the mission and impact, detailing the problem, solution, and funding strategies to achieve social goals.
- Example: A nonprofit improving literacy rates would outline programs, target communities, and impact measurement.
- Specialized business plans: Tailored for specific needs like securing loans or attracting investors, with a focus on financial sustainability and growth potential.
- Example: A business seeking a loan would create a plan highlighting its ability to repay, with detailed financial statements and projections.
Choosing the right plan type ensures effective communication of your business’s goals and strategies, increasing your chances of success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When creating a business plan, it’s crucial to avoid common pitfalls that can undermine your strategy and hinder your success. Here are some key mistakes to watch out for:
Overestimating Financial Projections
One of the most significant risks in business planning is being overly optimistic about your financial forecasts. While it’s important to have ambitious goals, overestimating revenue or underestimating expenses can lead to unrealistic expectations and financial strain. Investors and stakeholders are often skeptical of projections that seem too good to be true. Grounding your financial projections in realistic assumptions backed by historical data and market analysis is essential. This approach builds credibility and helps you avoid cash flow problems and financial shortfalls down the line.
Lack of Market Research
Market research is the foundation of a strong business plan. Without thorough research, you risk basing your strategy on assumptions rather than facts. Understanding your target market, competition, and industry trends is crucial for making informed decisions and positioning your business for success. A lack of market research can lead to missed opportunities, misaligned strategies, and failure to connect with your customers. Ensure that your business plan is backed by solid, up-to-date market data that supports your business model, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
Ignoring Potential Risks
Ignoring potential risks is a dangerous oversight in business planning. Every business faces uncertainties, whether they’re related to market conditions, competition, or operational challenges. Identifying and addressing these risks can leave your business vulnerable to unexpected setbacks. A comprehensive business plan should include a risk assessment outlining potential threats and the strategies you’ll use to mitigate them. By acknowledging risks upfront and planning for them, you can minimize their impact and ensure your business is better prepared to handle challenges.
Vague Goals and Objectives
Setting vague or overly broad goals is another common mistake in business planning. Goals that are not specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) can lead to a lack of direction and accountability. Without clear, measurable objectives, it’s difficult to track progress or determine whether your business is on the right path. Your business plan should include well-defined goals that provide a clear roadmap for achieving success. These goals should be broken down into actionable steps, with timelines and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor progress and adjust as needed.
You can create a persuasive business plan that effectively communicates your vision and strategy by addressing these areas.
Additional Resources and AI Tools
Creating a business plan can be a complex process, but numerous resources and AI tools are available to assist you. Here are a few that you may find helpful when writing your business plan:
Final Thoughts
Writing a comprehensive business plan is vital for any entrepreneur or business owner. It serves as a roadmap for your business and helps secure funding and attract investors. By understanding the different types of business plans and their specific uses, you can tailor your plan to meet your unique needs.
Avoid common mistakes such as overly optimistic projections, lack of research, ignoring weaknesses, and poor organization. Instead, focus on creating a clear, realistic, and well-researched plan that addresses potential challenges and outlines a solid strategy for growth.
FAQ
Who needs a business plan?
Anyone starting a new business, expanding an existing business, or seeking funding needs a business plan. It is essential for entrepreneurs, small business owners, and established businesses looking to set strategic goals and secure investment.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The 7 steps of a business plan include: Executive Summary, Company Description, Market Analysis, Organization and Management, Products/Services, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections.
Can I write a business plan myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan yourself. This guide provides you with a comprehensive step-by-step guide on writing a business plan for different types of businesses.
How many hours does it take to write a business plan?
Writing a business plan can take anywhere from 20 to 100 hours, depending on the complexity of the business, the amount of research needed, and the level of detail required. For more intricate plans to secure significant investment, expect to spend more time ensuring all aspects are thoroughly covered.
How long should a business plan be?
A business plan should typically be 15 to 30 pages, depending on your business size, industry, and purpose. A traditional plan with detailed financials and research will be longer, while a lean plan can be as short as 1–5 pages.
What are the three pillars of a business plan?
The three core pillars of a solid business plan are:
- Strategy: Your goals, vision, and business model.
- Market Understanding: Research on your industry, competitors, and target customers.
- Financial Planning: Revenue model, projections, funding needs, and profitability.
What are the three main structures of a business?
The three most common business structures are:
- Sole Proprietorship: Owned and operated by one person.
- Partnership: Owned by two or more individuals sharing responsibilities and profits.
- Corporation (or LLC): A legally separate entity offering liability protection and formal management structure.
Does Google Docs have a business plan template?
Yes, Google Docs offers free business plan templates through its template gallery.
Are there business plan templates?
Yes, we provide free business plan templates you can download and customize.
What does a real business plan look like?
A real business plan is a structured, well-organized document that includes:
- Executive Summary
- Company Overview
- Market Research
- Product or Service Description
- Marketing & Sales Strategy
- Financial Projections
- Funding Request (if applicable)
- Appendices with supporting documents