How to Calculate ROI: Essential Formulas, Excel Tips & Real Examples

Return on Investment (ROI) is one of the most critical metrics businesses use to measure the profitability and success of their investments. Whether it’s a marketing campaign, new technology, or employee training, knowing how to calculate and improve ROI can help businesses make smarter decisions and understand how much profit they are generating relative to their investments.
This is a basic formula that helps businesses measure the profit they are making from an investment. It’s a way to see if the money you’re spending is paying off. ROI is commonly used to evaluate marketing campaigns, new technology, or hiring new staff.
What is ROI?
Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial metric that measures the efficiency or profitability of an investment. It is a ratio that compares the gain or loss of an investment to its cost, providing a clear picture of how well an investment is performing. ROI is usually presented as a percentage and can be calculated using a straightforward formula:
ROI (%) = (Gain from Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment × 100
This formula helps businesses and investors understand the return on investment relative to the initial investment cost. For instance, if you invest $1,000 in a project and earn $1,200 in return, your ROI would be:
ROI = (1,200 – 1,000) / 1,000 × 100 = 20%
This means you have a 20% return on your investment. ROI is a crucial metric because it omits the time it took to earn a profit or make a loss, focusing solely on the efficiency of the investment.
Understanding the Importance of Streamling ROI Calculations
Streamlining ROI calculations is crucial for businesses and investors to make informed decisions quickly and accurately. By simplifying the calculation process, individuals can efficiently determine the return on investment of a particular investment, enabling them to compare the profitability of different investments. This streamlined approach helps identify the most lucrative opportunities and optimize investment portfolios.
Moreover, streamlined ROI calculations can highlight areas for improvement, allowing businesses to refine their strategies and enhance overall performance. By reducing the complexity and time required for ROI calculations, businesses can focus more on strategic decision-making and less on manual computations, ultimately driving better financial outcomes.
Key Components of ROI
To accurately calculate return on investment (ROI), several essential components should be considered. Each element helps in forming a clear picture of the investment’s financial impact, including both gains and costs:
- Net Profit: This represents the true profit derived from the investment after subtracting all relevant costs, indicating the actual financial gain or loss achieved. Net profit is a core measure of the investment’s success.
- Initial Investment Cost: This includes the original expenditure required to make the investment, covering purchase price, transaction fees, and any initial setup expenses. This cost serves as the baseline from which profits or losses are calculated.
- Total Gain from Investment: Encompassing all returns generated—both cash and non-cash—the total gain reflects the full range of benefits earned from the investment over time. This may include revenue, dividends, or asset appreciation.
- Ongoing Expenses: Beyond the initial cost, ongoing expenses (such as maintenance, upgrades, or operational costs) impact the investment’s total cost and can influence long-term ROI. These expenses are vital in understanding the investment’s continued impact on finances.
Evaluating these components provides a well-rounded view of an investment’s financial performance, allowing for more accurate and insightful ROI calculations. A precise understanding of ROI can help investors make informed decisions and optimize their investment strategies.
ROI Formulas: Understanding Return on Investment
Return on Investment (ROI) is a crucial metric for businesses, offering insight into the profitability of various investments relative to their costs. Whether it’s a marketing campaign, a new tool, or an operational upgrade, ROI helps businesses understand the financial impact and make informed decisions. Here’s a detailed look at key ROI formulas, examples, and how ROI supports strategic planning.
1. Basic ROI Formula
The basic formula for the ROI calculation, which is the simplest and most widely used, provides a percentage showing the profit relative to the initial investment cost.
ROI = Net Profit (or Gain from Investment)−Cost of Investment/Cost of Investment ×100
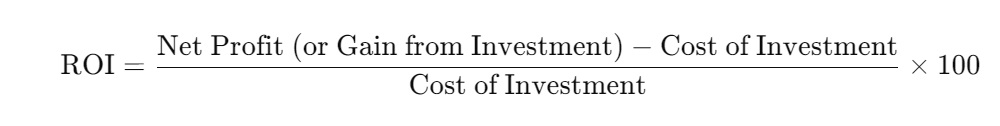
Explanation
- Net Profit (Gain from Investment): The revenue or profit generated from the investment.
- Cost of Investment: The total amount invested.
Example:
Suppose you invest $10,000 in inventory software, resulting in a net profit of $15,000:
ROI = (15,000-10,000)/10,000 * 100 = 50%
This 50% ROI indicates a substantial return, highlighting the profitability of the investment.
Applications:
This basic ROI formula helps businesses:
- Evaluate profitability: Identify which projects yield the highest returns.
- Compare different investments: Assess where resources are best allocated for maximum gain.
- Justify spending: Demonstrate where funds are well spent and where cuts might be made.
Key ROI Formulas for Businesses
Businesses can calculate ROI in various ways depending on the type of investment. Here are a few key formulas:
-
Basic ROI Formula: As mentioned earlier, the percentage return is calculated based on profit and cost.
ROI= [(Net Profit−Cost) / Cost] × 100 -
Annualized ROI: This is useful for long-term investments and shows the average return over a specific period.
Annualized ROI = (Final Value / Initial Value)^1/n −1Where n is the number of years.
-
ROI for Cost Savings: This focuses on investments that reduce operational costs rather than generate revenue.
ROI= [(Savings Achieved−Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment] ×100
Understanding whether an investment yields a positive or negative ROI is crucial for making informed financial strategies, as it quantifies the profitability and efficiency of investments.
Each of these formulas gives insight into how well an investment is performing, whether it’s a new product, an operational change, or a marketing push.
2. Annualized ROI Formula
For investments held over multiple years, the annualized ROI formula provides a more accurate picture by factoring in the investment’s time period. This calculation is particularly useful when comparing long-term investments or those held for varying durations.
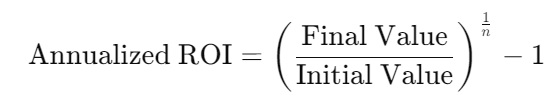
Where:
- Final Value: The value of the investment at the end of the holding period.
- Initial Value: The original investment cost.
- n: The number of years the investment is held.
Example:
If you invested $5,000 and the value after 3 years is $7,000:
Annualized ROI = (7,000/5,000)^1/3 – 1 ≈ 0.1187 or 11.87%
This calculation reflects an 11.87% average annual return over the three years, providing a clear perspective on yearly performance.
3. ROI for Cost Savings
While traditional ROI measures profit, many investments focus on reducing operational costs rather than generating revenue. In these cases, a cost-savings ROI formula is more relevant, as it highlights the efficiency gains achieved.
Formula:
ROI= [(Savings Achieved – Cost of Investment)/Cost of Investment]×100
Example:
If a $10,000 investment in process automation yields $12,000 in savings:
ROI=[(12,000−10,000)/10,000]×100=20%
This indicates a 20% return based on the cost savings alone, showcasing how operational efficiency contributes to profitability.
Importance of Streamlined ROI Calculations
Accurately calculating ROI is not just about saving time; it’s about improving decision-making, increasing financial transparency, and driving growth. A streamlined ROI process allows businesses to:
- Enhance Accuracy: Reduces errors, offering reliable insights.
- Enable Data-Driven Decisions: Supports financial planning and resource allocation.
- Facilitate Future Strategy: Helps shape future business goals based on sound financial performance.
Incorporating these ROI calculations into decision-making processes ensures businesses gain a clear picture of their financial health, enabling them to optimize investments and sustain long-term growth.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating ROI
ROI calculation can be easy if done right. Here’s a simple guide to measure ROI effectively and efficiently.
Step 1: Identify the Costs
Start by making a list of all the expenses related to your investment. Make sure it’s comprehensive. This includes initial outlays, ongoing operation costs, and maintenance expenses. Consider any other financial commitments required to sustain the investment. This includes both direct and indirect costs.
Direct costs are those that can be attributed to the investment. The purchase price or installation fees would be an example. Indirect costs would be overheads or administrative fees.
Opportunity costs are also an important consideration. What are you giving up on by choosing this investment over another? Accurate cost identification forms the baseline for calculating ROI.
Step 2: Calculate the Returns
This next step involves determining the financial gains or revenue from your investment. Returns can come in forms such as income generated, increase in asset value, cost savings, or other financial benefits.
For longer-term investments, consider the time value of money. Future returns may need to be discounted to accurately present their worth.
Step 3: Use the Return on Investment Formula
The basic return on investment formula for calculating ROI is (Gain from investment—cost of investment)/cost of investment x 100.
Subtract the total costs from the total return to find the net gain or loss. Then divide this net gain by the total cost of the investment. This gives you the ROI as a decimal. To convert it into a percentage, multiply by 100. This percentage is a clear way to see your investment in relation to your cost.
Step 4: Analyze the Results
Now that you have your ROI percentage, what does that mean for your investment? A higher ROI generally means a higher return on investment. This should still be compared to industry standards. Alternative investment opportunities should also be considered. The time frame of the ROI should also be looked at, with a longer period being less impressive in general.
Risks associated with the investment should also be taken into account. Higher returns generally come with higher risks.

Calculating ROI in Excel
Using Microsoft Excel to calculate ROI can significantly streamline the process, especially for handling complex calculations and investments with varying time periods and returns. Excel offers built-in formulas and functions that allow you to automate calculations, visualize data with charts, and perform what-if analyses to forecast potential outcomes.
With Excel, you can organize and store data over time, making tracking and analyzing ROI trends easy. This approach enhances accuracy and enables a more dynamic view of your investments, allowing for informed decision-making and ongoing financial performance tracking.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating ROI in Excel
Excel provides various tools to simplify ROI calculations. Follow these steps to calculate ROI effectively:
1. Set Up Your Spreadsheet
- Open Excel and create a new worksheet.
- In Column A, label the cells as follows:
- A1: “Initial Investment”
- A2: “Final Value”
- A3: “Time Period (Years)” (optional if calculating annualized ROI)
- A4: “Net Profit” (optional if you prefer to calculate this manually)
- A5: “ROI (%)”
- A6: “Annualized ROI (%)” (if needed)
2. Input Values
- Cell B1: Enter your initial investment amount.
- Cell B2: Enter the final value or the gain from your investment.
- Cell B3: Enter the time period in years (only needed if calculating annualized ROI).
3. Calculate Net Profit
- In Cell B4: Type
=B2 - B1and press Enter. This calculates the net profit or gain from your investment.
4. Calculate Basic ROI
- In Cell B5: Type the formula
=(B4 / B1) * 100and press Enter. This will calculate the ROI percentage. - Your basic ROI calculation is now complete. The result in Cell B5 represents the return on investment as a percentage.
5. Calculate Annualized ROI (Optional)
- In Cell B6: Type the formula
=((B2 / B1)^(1 / B3)) - 1and press Enter. - This formula calculates the annualized ROI, which is useful for investments with a long-term time horizon.
- Format Cell B6 as a percentage to see the ROI in percentage terms.
6. Customize with Excel’s Built-In Functions
- Use Excel’s
What-If Analysistool to test different initial investments, final values, or time periods. Access this tool by going to:- Data > What-If Analysis > Goal Seek
- You can adjust variables to see how changes affect ROI, which is especially useful for forecasting.
7. Create Visuals for Trend Analysis
- Highlight your ROI data (e.g., ROI and Annualized ROI percentages over time if tracking multiple investments).
- Go to Insert > Charts to create a visual representation, such as a line or bar chart. This can help you easily interpret ROI trends over time.
With this setup, Excel allows you to automate, store, and monitor ROI data, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in your financial analysis. This approach makes updating inputs for quick recalculations easy, providing a comprehensive tool for your ongoing investment analysis.
Interpreting ROI Results
Interpreting ROI results is crucial for understanding an investment’s profitability and efficiency. A positive ROI indicates that the investment generates a profit, while a negative ROI signifies a loss. The ROI percentage shows how high the return is on the investment costs.
For example, a 20% ROI means the investment generated a 20% return on the initial investment cost. This information is vital for making informed decisions about future investments. A higher ROI generally suggests a more profitable investment, but it’s also important to consider the associated risks and compare the ROI against industry benchmarks and alternative investment opportunities.
By understanding and interpreting ROI results, businesses can make strategic decisions that enhance profitability and drive long-term growth.
Why is ROI Important for Businesses?
- Measure Success: ROI helps you determine whether an investment, such as a marketing campaign or new equipment, is making money.
- Compare Options: It lets you compare different investments and choose the one that will give you the best return.
- Justify Spending: It provides clear data to support decisions, especially when explaining investments to stakeholders or team members.
Ways to Improve ROI
- Cut Costs: Find ways to lower the cost of investments without sacrificing quality.
- Increase Profit: Focus on strategies that increase revenue, such as targeting the right customers or optimizing your sales process.
- Use Automation: Tools like inventory management software or customer relationship management (CRM) systems can improve efficiency and reduce errors, increasing ROI.
In short, ROI is a simple but powerful tool that helps businesses make better decisions about where to invest time and money. It shows how much you’re getting back for every dollar you spend, helping you maximize profitability.
How to Use ROI in Business Decision-Making
ROI is a powerful tool for guiding business decisions. Here’s how businesses can use it effectively:
- Prioritizing Investments: When deciding where to invest time and money, ROI helps you choose the option with the best return. If two projects have different costs and returns, ROI helps you compare them on an equal footing.
- Comparing Multiple Projects: ROI allows you to evaluate the profitability of different projects, helping you decide which ones to pursue and which to put on hold.
- Real-time Adjustments: By regularly tracking ROI, businesses can adjust their strategies on the fly. For example, if a marketing campaign isn’t delivering the expected ROI, you can cut costs or pivot your approach.
- Balancing Short-term and Long-term ROI: Not all investments generate immediate returns. ROI helps you evaluate whether a long-term investment, like employee training or technology upgrades, is worth the initial cost.
Factors that Affect ROI
Several factors can impact your ROI calculations, making it important to consider the following:
- Costs: Make sure to include all direct and indirect costs (labor, materials, etc.) in your ROI calculations.
- Time Frame: The time period over which you evaluate an investment will influence your ROI. Long-term projects often show better ROI over time.
- External Factors: Market conditions, competition, and customer demand can all affect the return you get from your investments.
- Risk: ROI does not always factor in the risk associated with an investment, so you should also consider the potential downside.
The Limitations of ROI
While ROI is a powerful tool, it does have its limitations:
- Intangible Benefits: ROI doesn’t always measure things like brand loyalty, employee satisfaction, or market positioning. These benefits can be crucial but difficult to quantify.
- Short-Term Focus: If you only focus on short-term ROI, you might miss out on long-term opportunities that could bring significant value in the future.
- Ignoring Risk: Basic ROI calculations don’t account for risk, which is why businesses often complement ROI with other financial metrics like Net Present Value (NPV) or Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
Advanced ROI Analysis Tools and Metrics
For more accurate decision-making, many businesses go beyond basic ROI by using advanced tools like:
- Net Present Value (NPV): This measures the present value of future cash flows from an investment, accounting for the time value of money.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): IRR shows the expected rate of return for a project over its lifetime, which helps businesses evaluate long-term investments.
- Payback Period: This measures how quickly an investment will pay for itself, which can be important for businesses with cash flow concerns.
Maximizing ROI for Business Growth
Finally, businesses can maximize ROI by following these strategies:
- Improve Efficiency: Streamlining operations and reducing waste will improve ROI by lowering costs.
- Leverage Technology: Using the right tools (like CRM systems, inventory management software, etc.) can improve productivity and yield higher returns.
- Focus on High-Return Activities: Regularly review your business activities to focus on those with the highest ROI, such as customer retention programs or targeted marketing campaigns.
- Monitor Continuously: Regularly track and review your ROI metrics to ensure you get the most out of your investments and make adjustments when necessary.
Key Features to Look for in ROI Analysis Tools
Looking for tools for ROI data analysis? The main focuses should be user-friendliness, accuracy, and the ability to handle complex data. The right tool should simplify the process—not complicate it. Seek features that allow for easy data input and clear result reporting.
Top Tools and Software for Streamlining ROI Calculation
There are endless tools with features to help streamline your ROI calculation process. Automated calculations, data visualization, and integrations with other financial systems are just a few. Each tool has its advantages, so choose one that aligns with your specific needs.
Case Studies: Real-World ROI Calculation
Understanding how businesses in various sectors calculate ROI can be invaluable. This holds true for small startups as well as large corporations. Case studies emphasize the practical application of ROI calculation techniques and highlight their impact on business decisions.
One example is a small online retail business that invested $5,000 in advertising. Over 3 months, the campaign brought an extra $15,000 in sales. Using the ROI formula, the return on investment is such ($15,000 – $5,000)/ $5,000 x 100 = 200. This ROI shows the campaign’s success and can guide future marketing investments.

Conclusion
Mastering ROI calculation is essential for making smart business decisions. This process can easily improved with the right tools and techniques. It will also give you a clearer picture of your business performance. Keep in mind that the goal isn’t just ease – but also optimal growth and success.
FAQ
Q1: Can ROI be negative?
A1: Yes, ROI can be negative. This indicates that the investment resulted in a loss, rather than a profit.
Q2: What are ROI tools?
A2: ROI tools are software or calculators. They help businesses efficiently calculate the return on investment.
Q3: What are ROI strategies?
A3: ROI strategies are methods to maximize return on investment. These focus on optimizing costs and enhancing revenue.