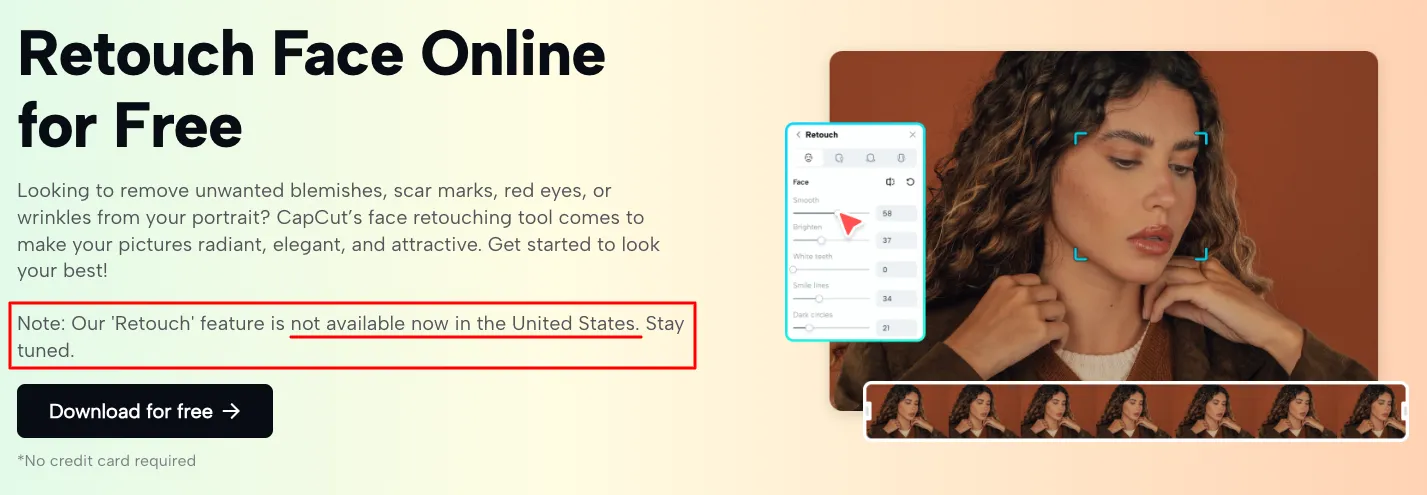
What Is an AI Agent? A Practical Overview for SMBs

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer exclusive to large enterprises. Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) leverage AI to streamline operations, cut costs, and boost productivity. One of the most accessible and powerful ways to do this is by implementing AI agents.
This overview introduces AI agents, explains their value for SMBs, and highlights who can benefit from them. It also outlines the tools you’ll need to get started.
What is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a digital system capable of performing tasks, making decisions, and interacting with data or tools without constant human input. Unlike traditional automation, which follows rigid rules, AI agents adapt in real time. They use artificial intelligence to interpret context, generate insights, and take action.
Insight: Think of it as a digital teammate that doesn’t need sleep, takes feedback seriously, and becomes more helpful the more you use it.
For example, an AI agent can:
- Read and categorize emails
- Draft contextual responses
- Sync with calendars and CRMs
- Route leads to sales team members
- Summarize complex documents
Why AI Agents Matter for SMBs
Before you build AI agents, it’s important to understand why they’re such a game-changer for small and mid-sized businesses. This section explores AI agents’ concrete advantages, from customer support to marketing and decision-making.
- Save Time and Boost Productivity
AI agents handle repetitive, manual tasks quickly and accurately, allowing your team to focus on higher-value, strategic work. - Reduce Costs
Replacing time-intensive tasks with smart automation lowers labor costs and increases operational efficiency. - Deliver Better Customer Experiences
Faster response times, personalized messaging, and consistent follow-ups lead to happier customers and stronger relationships. - Make AI Accessible to Everyone
With no-code tools like n8n.io, anyone can build and manage AI agents. No programming knowledge is required. - Stay Competitive
AI agents empower smaller teams to perform at a higher level, closing the gap with larger competitors through smart automation.
AI agent vs. AI assistant vs. bot
Many business owners confuse AI agents with assistants and chatbots. This section breaks down the differences so you can choose the right tool for your needs.
| Feature | AI Agent | AI Assistant | Chatbot |
| Autonomy | High – Acts independently based on goals and tools | Medium – Responds to tasks but needs prompting | Low – Follows fixed scripts or flows |
| Adaptability | Learns from interactions and improves | May improve slightly or with training | Does not learn or adapt |
| Complexity | Can execute multi-step, cross-platform tasks | Good for simple tasks or voice commands | Handles single-turn interactions |
| Example | AutoGPT, LangChain agents | Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant | Support widget bots, FAQ bots |
Types of AI agents
AI agents come in different flavors. This section outlines the key types to understand their capabilities and choose the right one for your business use case.
-
Reactive Agents – Respond to stimuli without memory. Great for quick, stateless decisions like spam detection.
-
Deliberative Agents – Use logic and internal planning to decide the best course of action. This is helpful for goal planning and optimization.
-
Learning Agents – Improve with feedback. Perfect for environments where performance should adapt over time.
-
Collaborative Agents / Multi-Agent Systems – These systems allow agents to collaborate with other agents to complete larger workflows. They are great for task division (e.g., sales + research) and especially useful for orchestrating multi-functional processes.
-
Generative AI Agents – Use LLMs like GPT-4 to create new content such as emails, summaries, or code.
Who Can Use AI Agents?
Wondering how you’d use AI agents in real business scenarios? This section showcases specific applications across departments.
Business Owners
-
Automatically summarize customer insights
-
Schedule meetings and manage inboxes
-
Generate weekly performance reports
Marketing Teams
-
Repurpose content across channels
-
Monitor competitor activity
-
Analyze campaign performance
Sales Professionals
-
Qualify and route leads
-
Personalize outreach messages
-
Update CRM entries automatically
HR and Operations Teams
-
Screen resumes and schedule interviews
- Organize internal requests efficiently
Customer Support Agents
- Handle frequently asked questions
- Prioritize support tickets
- Log conversation data in real-time
Tools You Need to Build AI Agents
Here’s a simple tech stack to build your first AI agent:
| Tool | Purpose |
| n8n.io | No-code platform to build workflows and manage agents |
| OpenAI, Claude, Gemini | AI models for text generation and decision-making |
| Gmail, Slack, Airtable, Google Calendar | Services that serve as triggers, data sources, or action outputs |
What You Can Do with AI Agents
Here are a few real-world use cases that are especially useful for SMBs:
| Use Case | Description |
| Lead Sorter | Scores and routes leads based on form submissions or email inquiries |
| Email Assistant | Categorizes messages and drafts responses using your calendar and goals |
| Content Repurposer | Turns long-form content into short-form posts or newsletters |
| Meeting Scheduler | Coordinates calendars automatically between team and clients |
| Customer Support Bot | Responds to basic queries and escalates issues as needed |
| Research Assistant | Gathers online information and summarizes it in structured formats |
Related Articles





Benefits of AI agents for SMBs
AI agents don’t just save time. They make your business more agile, data-driven, and customer-friendly.
| Benefit | Description |
| Time Savings | Automate routine tasks to free up employee hours. |
| 24/7 Availability | Offer customer and internal support any time, even overnight. |
| Lower Costs | Reduce the need for manual labor or outsourced services. |
| Personalization | Deliver more relevant experiences based on user history. |
| Data-Driven Insights | Turn data into actionable business intelligence. |
| Competitive Advantage | Compete with larger companies using smarter tools. |
Risks & how to handle them
While powerful, AI agents are not without risks. This section covers common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
-
Security: Protect sensitive customer and business data.
-
Hallucinations: Ground the agent in your verified knowledge base.
-
Bias: Review responses and data sources regularly.
-
Over-reliance: Always offer a human fallback when necessary.
-
Integration Bugs: Test all third-party tools carefully.
Integration with existing systems and tools
Successful AI agents don’t operate in isolation. This section provides a playbook for integrating them with your CRM, email, calendar, and other critical platforms.
-
Use APIs to connect agents to tools like HubSpot, Salesforce, Google Calendar, Outlook, and Shopify.
-
Leverage native integrations in no-code platforms to simplify workflows.
-
Ensure data synchronization between tools to prevent errors or duplication.
-
Create fallback logic so that the agent reroutes or escalates to a human if a tool fails.
Tip: Start with one integration (e.g., CRM) and test its reliability before adding others.
Future Trends in AI Agents
The AI agent landscape is evolving fast. This section offers a glimpse into what’s next and how SMBs can prepare.
-
Memory-Enhanced Agents: Newer agents can remember past interactions for deeper personalization.
-
Multi-Agent Orchestration: Agents will increasingly work together across tasks and departments.
-
Voice-Enabled Agents: Expect smoother voice integrations, enabling more natural interfaces.
-
Industry-Specific Agents: More AI agents will emerge pre-trained for healthcare, real estate, or finance niches.
Prepare by choosing tools with upgrade paths and scalable integrations.
Final Thoughts
AI agents represent a major opportunity for SMBs to improve productivity, reduce overhead, and provide better service. With the rise of no-code tools, building these systems is now within reach for nearly any business professional.
This overview gives you the foundation to understand how AI agents work and why they matter.
FAQs
How long does it take to build an AI agent?
No-code: 1–3 days. Framework-based: 1–3 weeks. The actual time depends on complexity, integrations, and how polished you want the experience to be.
Do I need coding skills?
No, if you use tools like CustomGPT or Voiceflow. Yes, if you’re using LangChain, LlamaIndex, or doing multi-agent orchestration.
Can I use AI agents internally?
Yes! Internal use cases like HR support, IT helpdesk, document summarization, or internal training assistants are often the best places to start.
How much does it cost?
Basic use: <$100/month. Advanced agents (e.g., multi-tool, multi-agent systems) could require $500–$5,000/month depending on usage, tool stack, and developer resources.
Can AI agents connect to my CRM or calendar?
Yes. Most tools offer out-of-the-box integrations with Gmail, Outlook, HubSpot, Salesforce, and more. Others may require API keys or custom connectors.
How do I ensure the agent doesn’t give wrong answers?
Use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to ground responses in your documents. Also, set clear limits in the agent’s prompt to avoid speculation.
What are common mistakes when building AI agents?
Skipping the strategy phase, overloading the agent with tasks, ignoring user feedback, and failing to test edge cases.
How do I monitor agent performance?
Use dashboards (many platforms have them), review chat logs, implement thumbs up/down feedback, and track KPIs like resolution rate or task completion.
Can I train the agent on my proprietary documents?
Yes. Most platforms let you upload PDFs, text files, and URLs and embed them into a vector database for the agent to reference.
Will customers know they’re speaking to an AI?
They should. Best practice is to make that transparent and offer an option to escalate to a human if needed.