What Is an SKU Number? And How to Leverage It

In the world of retail, organization is key, especially when managing a variety of products. That’s where SKU numbers come into play. A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a scannable code retailers use to identify and track a product, ensuring smooth inventory management and accurate sales tracking. But what exactly is an SKU number, and how can it help your business?
Whether you’re a small business owner, a seasoned retailer, or operate an e-commerce business, understanding SKU codes can improve customer satisfaction and boost sales efficiency.
In this article, we’ll break down the basics of product SKUs, explore their importance, and answer common questions like how many digits an SKU number has and where to find an SKU number for your products. Let’s dive in!
What Is an SKU Number?
An SKU number (Stock Keeping Unit) is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to each product in your inventory. Retailers and e-commerce vendors use these codes to identify, track, and manage their stock efficiently. Think of an SKU code as a fingerprint for your products — it differentiates one item from another based on factors like size, color, style, or model.
Unlike barcodes — which are universal — product SKUs are created by businesses and are specific to their inventory. This flexibility allows retailers to customize SKUs to include meaningful information about the product, streamlining processes such as stock replenishment and sales reporting.
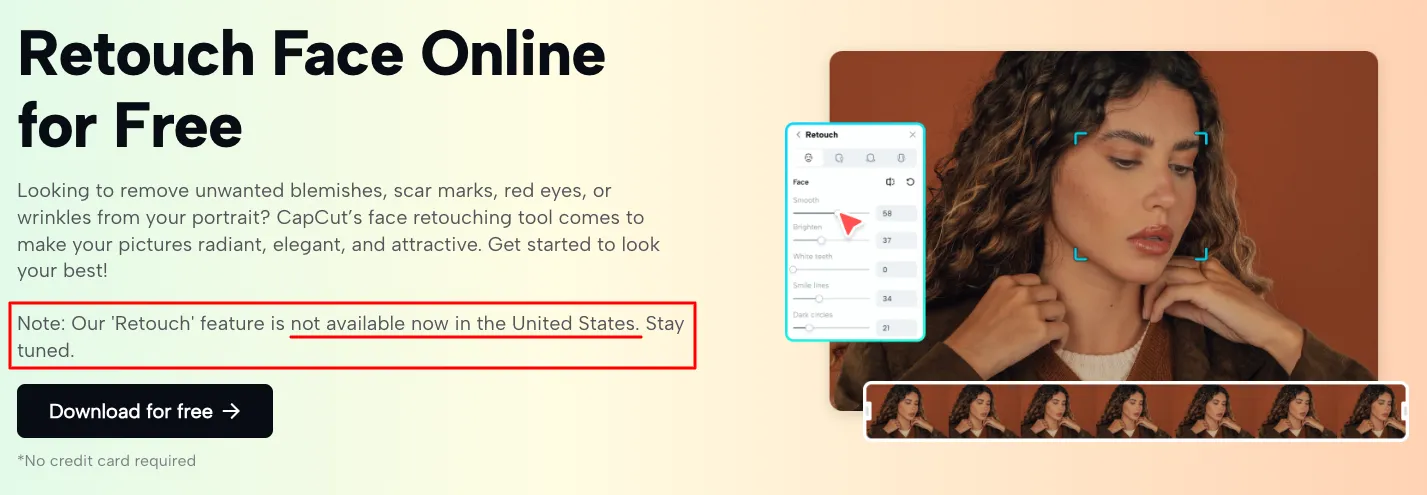
Typically, an SKU number can range from 8 to 12 characters, though the length may vary depending on the complexity of your inventory management system. For example, an SKU for a medium-sized black t-shirt might look something like BLK-T-MED-246.
These codes help businesses maintain order in their inventory, making it easy to locate and track items both in-store and online. An SKU number is a vital component of any successful inventory system, ensuring your products are easily identifiable and traceable at all times.
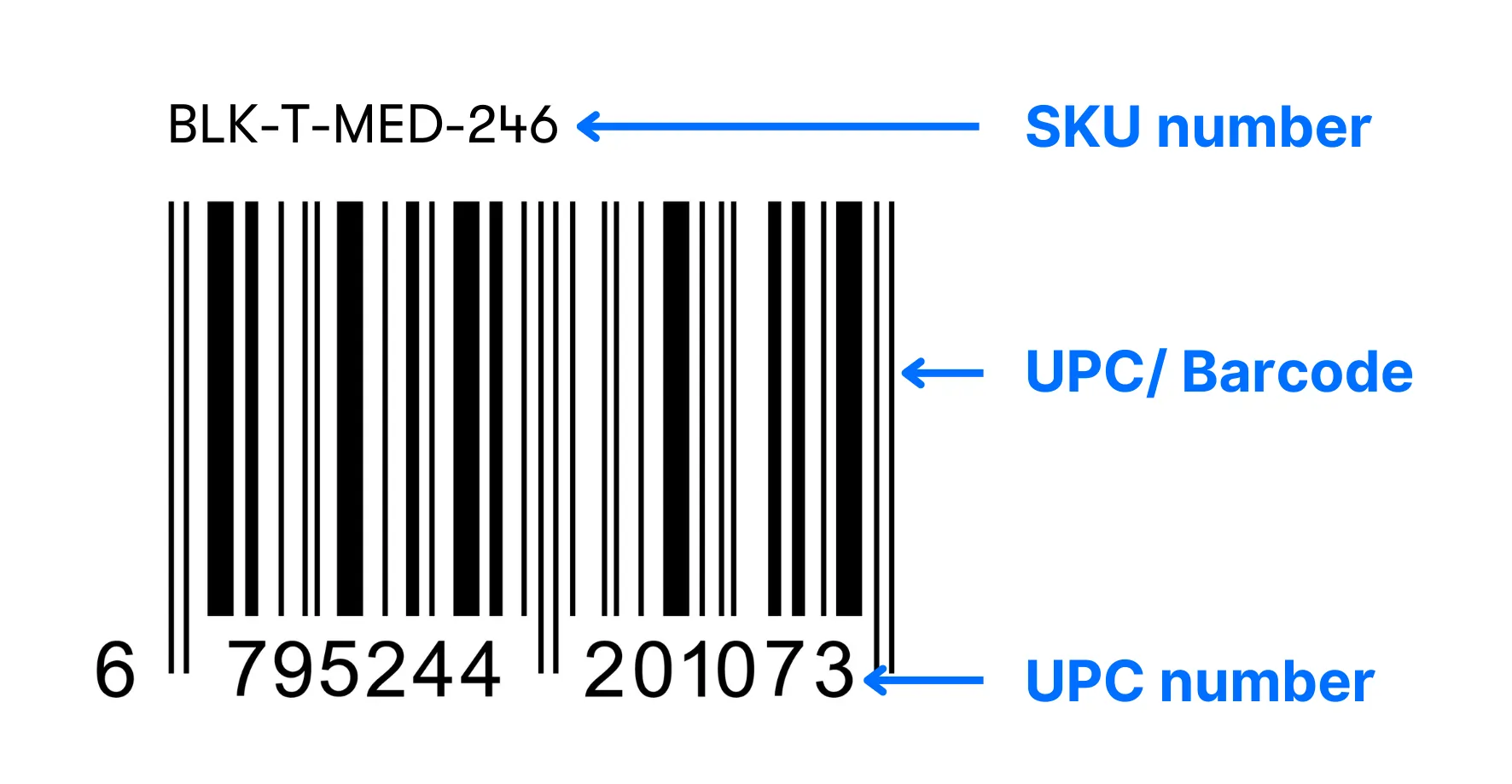
What is an SKU vs. a UPC Number?
A UPC number (Universal Product Code) is a standardized 12-digit numeric code with a barcode used globally to identify and track products across retailers and supply chains. Unlike SKU numbers, which businesses customize for internal inventory management, UPCs are universal identifiers that ensure consistent product recognition across industries.
Where to Find SKU Numbers
Finding SKU numbers is easy once you know where to look. Here are the most common places:
- Product packaging: Check the packaging for a small printed number or label.
- Receipts: Many receipts list the SKU number next to the product description.
- Price tags: In-store items often display their SKU numbers on price tags.
- Inventory systems: Your inventory management or point-of-sale (POS) system will have all your SKU numbers stored.
- Online listings: Sites like Amazon and eBay often show SKU numbers in the product details section.
How Does an SKU Number Work?
An SKU number works as a unique identifier that helps businesses organize, track, and manage their inventory efficiently. Here’s how it functions:
- Customization: Businesses create SKU numbers tailored to their specific needs. Each number can encode details such as product category, size, color, or location.
- Product identification: SKU numbers distinguish individual product variations, even when items are similar. This ensures that each product is easily identifiable within the inventory system.
- Inventory management: By scanning or referencing SKU numbers, businesses can locate products quickly and track stock levels in real-time.
- Sales tracking: SKU numbers allow retailers and e-commerce vendors to track sales for each specific product.
- Integration with software: Inventory management systems rely on SKU numbers to maintain accurate digital records of stock levels and sales.
- Operational efficiency: Employees can use SKU numbers to locate products faster, whether in a physical store, warehouse, or during order fulfillment, reducing time and errors.
SKU numbers act as a cornerstone of inventory organization, giving businesses the tools they need to maintain control over stock, improve sales analysis to boost sales, and deliver better service to customers.
Why Is an SKU System Important?
A well-organized SKU system is vital for retailers and e-commerce vendors to manage inventory. But beyond tracking inventory — it’s a strategic asset that empowers businesses to optimize operations, improve customer satisfaction, and make data-driven decisions.
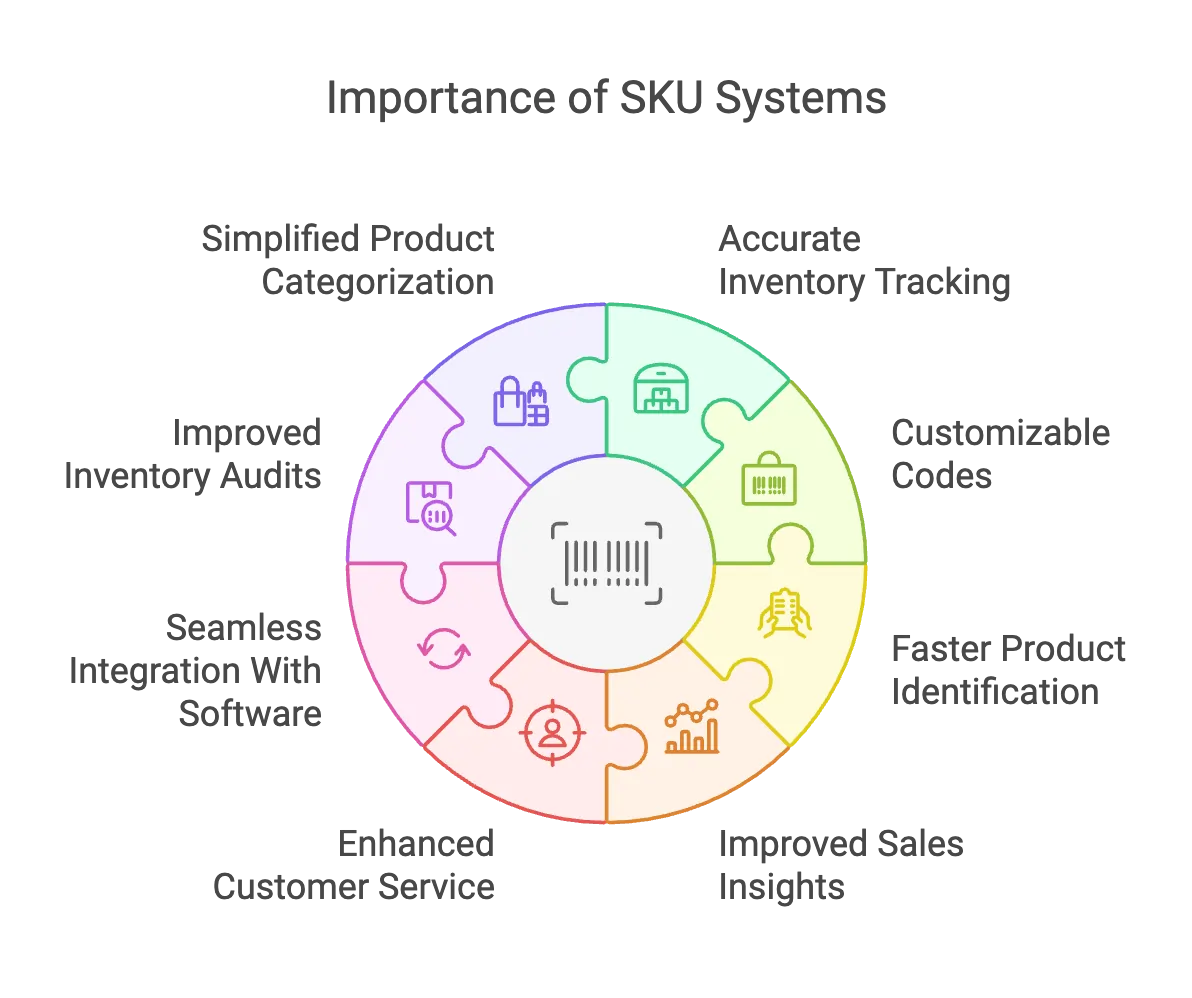
Here’s how implementing SKU numbers makes a difference:
1. Accurate Inventory Tracking
An SKU system helps businesses monitor stock levels precisely, reducing the chances of overstocking or stockouts and streamlining reordering. By tying SKU codes to specific products, businesses can streamline restocking and ensure that popular items remain available to customers.
For example, tools like Lightspeed POS enable businesses to set reorder points so products are automatically added to a reorder list when stock hits a minimum threshold.
- Tip: Regularly review and update your inventory records to ensure the data tied to each SKU number remains accurate.
Recommended Inventory Management Software
Zoho – Cloud-based inventory management solution
Epicor – Built-in inventory analytics in real-time
Square – Manage inventory across multiple locations
2. Customizable Codes
SKU codes can be tailored to include meaningful information about a product, such as its size, color, or style. This level of detail makes it easier to differentiate similar products and keeps your inventory organized. For instance, a retailer might use an SKU like PNK-T-MED to represent a pink medium-sized t-shirt.
- Tip: Create a consistent structure for your SKU numbers to ensure they are intuitive and easy to manage.
3. Faster Product Identification
Knowing where to find an SKU number — typically on product tags, packaging, or inventory systems — enables employees to quickly locate items in-store or in a warehouse. This speeds up daily operations like restocking, packing, and fulfilling orders. For example, PNK-T-MED would be that pink T-shirt in medium size, vs. PNK-LT-MED, which would be a long T-shirt.
- Tip: Train employees to recognize and utilize SKU codes effectively to save time and reduce errors during inventory searches.
4. Improved Sales Insights
Analyzing sales data tied to SKU numbers provides valuable insights into which products are best-sellers and which ones are underperforming. This helps businesses make informed decisions about promotions, discounts, and inventory replenishment.
- Tip: Use inventory management software to track sales performance using SKU codes for actionable insights.
5. Enhanced Customer Service
A clear SKU system ensures faster and more accurate order fulfillment, improving the customer experience. Whether customers are shopping in-store or online, organized SKU numbers help locate and deliver products efficiently.
- Tip: Highlight key SKU codes for popular items to streamline the fulfillment process during peak sales periods.
6. Seamless Integration With Software
Retail SKUs integrate seamlessly with inventory management systems, providing real-time insights on stock levels and sales trends. This ensures smooth operations across physical stores and e-commerce platforms.
- Tip: Choose inventory software that supports custom SKU codes and multi-channel synchronization.
7. Improved Inventory Audits
Conducting inventory audits becomes more efficient with a structured SKU system, as each product has a unique identifier. This reduces the likelihood of errors during stock counts and helps save time. It also ensures you’re not overstocked with unpopular items, reducing your warehouse management costs.
- Tip: Schedule regular inventory audits to ensure the accuracy of your SKU system and prevent discrepancies.
8. Simplified Product Categorization
Using SKU codes to categorize products by size, color, or type makes it easier to organize stock. This is particularly helpful for businesses with diverse product ranges.
- Tip: Group SKU numbers logically, such as by product type or seasonality, to simplify sorting and inventory checks.
9. Support for Multi-Channel Sales
Consistent SKU numbers allow businesses to manage inventory seamlessly across multiple sales channels, such as physical stores, e-commerce websites, and marketplaces. This ensures stock accuracy and prevents overselling.
- Tip: Use the same SKU codes across all platforms to maintain consistency and avoid confusion.
10. Enhanced Loss Prevention
Tracking specific product SKUs helps businesses identify discrepancies between recorded stock levels and physical counts, reducing the risk of theft or shrinkage.
- Tip: Set up alerts in your inventory system to flag unusual stock movements tied to certain SKU numbers.
11. Better Forecasting
Analyzing sales patterns associated with retail SKUs allows businesses to predict future demand. This ensures stock availability without over-purchasing, reducing waste and maximizing profits.
- Tip: Use historical data from your SKU system to plan seasonal inventory and avoid supply chain management disruptions.
SKU Number Example
Let’s take the example of a pair of blue running shoes, size 10. A retailer might assign it an SKU number like this:
SH-RUN-BLU-10
Here’s how the components of this SKU number break down:
- SH: Represents the product category (shoes).
- RUN: Indicates the product type (running shoes).
- BLU: Denotes the color (blue).
- 10: Specifies the size (10).
This unique SKU number identifies this specific product variation, ensuring it stands out among other shoe options. If the same running shoe is available in a different size or color, it would have a different SKU, such as SH-RUN-BLU-9 for a size 9 or SH-RUN-RED-10 for a size 10 in red.
Using this SKU code, the retailer can:
- Track the stock of size 10 blue running shoes separately from other variations
- Analyze which sizes and colors are selling best
- Reorder specific variations without confusion
Tip: When creating SKU numbers, ensure they are concise and descriptive so both your team and systems can easily understand and use them.
How to Create SKU Numbers
Creating effective SKU numbers is essential for organizing and managing inventory efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating SKU numbers:

1. Define Key Attributes of Your Products
Start by identifying the main characteristics that differentiate your products, such as:
- Product category or type
- Size or dimensions
- Color or style
- Brand or model
Example: For a red, medium-sized dress, the key attributes might be:
- Category: Dress
- Size: Medium
- Color: Red
2. Create a Consistent Structure
Establish a standardized format for your SKU numbers that works across your entire product catalog. Common formats include:
- [Category]-[Color]-[Size] (e.g., DRS-RED-MED)
- [Brand]-[Type]-[Color]-[Size] (e.g., NIKE-SH-BLU-10)
Keep the structure simple and logical so it’s easy for your team to understand and use.
3. Use Short Codes for Each Attribute
Use abbreviations or codes for each attribute to keep SKU numbers concise. Avoid using full words, which can make SKUs overly long.
- Category: Dress → DRS
- Color: Red → RED
- Size: Medium → MED
Tip: Make sure the codes are intuitive and consistent across your inventory.
4. Avoid Confusing Characters
Avoid using characters that could be misread, such as:
- Letters and numbers that look similar (e.g., O and 0, I and 1).
- Special characters like slashes (/) or spaces, which some systems may not support.
Instead, stick to letters, numbers, and simple separators like dashes or underscores if needed.
5. Incorporate Unique Identifiers
Ensure that each SKU is unique to avoid duplication or confusion. If you have variations of the same product (e.g., different colors or sizes), assign a distinct SKU for each variation.
6. Test for Scalability
Make sure your SKU system can accommodate new products as your inventory grows. A flexible format allows you to easily add SKUs for new product lines or attributes without reworking your entire system.
7. Implement and Document Your SKU System
Once you’ve finalized your SKU structure, document the rules and share them with your team. Consistency is key to maintaining an effective SKU system.
8. Example of a Well-Structured SKU
For a brand called “ActiveFit,” selling a blue, size 10 running shoe, the SKU might look like:
AF-SH-RUN-BLU-10
- AF: Brand (ActiveFit)
- SH: Category (Shoes)
- RUN: Type (Running)
- BLU: Color (Blue)
- 10: Size (10)
Tips for Creating SKU Numbers
- Keep them concise but descriptive enough to differentiate products.
- Ensure SKUs are unique to prevent errors in inventory tracking.
- Regularly review and update your SKU system as your inventory evolves.
- Use inventory management software to streamline the creation and use of SKUs.
By following these steps, you can build an organized SKU system that simplifies inventory management and supports business growth.
Practical Uses and Benefits of SKUs
SKU numbers play a vital role in helping retailers and e-commerce vendors manage inventory, optimize sales, and enhance customer satisfaction. Apart from inventory management, here’s how businesses use SKU numbers in their day-to-day operations:
1. Forecast Sales
Tracking inventory using SKU numbers enables businesses to anticipate future demand and stock up accordingly. By analyzing sales trends tied to SKUs, merchants can determine which products are most in demand.
However, it’s essential to maintain a balanced inventory and not exclusively focus on top sellers—customers often value variety, and eliminating certain products could lead to lost business, as demonstrated by Walmart’s “Project Impact” in 2008.
- Tip: Use SKU sales data to predict demand, but ensure less popular products remain available to retain loyal customers.
2. Capitalize on High-Profit Products
By analyzing SKU data, businesses can identify their most profitable and popular products. This allows them to strategically display these items in-store, online strategically, or in marketing campaigns to maximize sales.
For example, crafting eye-catching product displays for seasonal best-sellers can boost customer interest and drive purchases.
- Tip: Use SKU reports to craft promotions and highlight best-selling items, especially during peak sales periods.
3. Recommend Relevant Products
SKU numbers often encode characteristics like size, color, and type, making them a powerful tool for personalized recommendations. If a product is out of stock, sales associates can use SKU data to suggest alternatives with similar attributes.
Online, this same principle drives cross-selling through “other products you may like” recommendations.
- Tip: Train your staff to use SKU data for in-store recommendations and configure your e-commerce platform to leverage SKU-based product suggestions.
4. Simplify Returns and Exchanges
When customers return or exchange products, SKU numbers make it easy to identify the exact item and update inventory records. This speeds up the process, ensuring a positive customer experience while keeping stock levels accurate.
- Tip: Include SKU numbers on receipts and order confirmations to make returns and exchanges seamless for both customers and staff.
5. Enhance Marketing Strategies
By analyzing SKU sales data, businesses can identify high-performing products to feature in marketing campaigns. For example, you can bundle slow-moving items with best-sellers or promote trending products through seasonal discounts to boost sales.
- Tip: Use SKU insights to tailor your marketing strategies, focusing on what resonates most with your customers.
6. Facilitate Supplier Communication
SKU numbers simplify conversations with suppliers by providing a clear reference for the exact products you need to reorder. This reduces the risk of errors or misunderstandings during the procurement process and is especially beneficial during peak shopping seasons.
- Tip: Share your SKU structure with suppliers to improve efficiency and ensure accurate product orders.
7. Monitor Product Performance Over Time
SKU numbers allow businesses to track product performance over the long term, helping to identify seasonal trends and consistent year-round demand. It’ll also help establish the longevity of the product’s demand and when to introduce new products to your customer base.
This data informs better decisions on which products to keep, promote, or discontinue.
- Tip: Regularly review historical SKU data to optimize your product offerings and refine your inventory strategy.
By leveraging SKU numbers effectively, your business can streamline operations, boost sales, and create a more satisfying experience for your customers. An organized SKU system is a key asset for long-term success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid With SKU Numbers
Creating and managing SKU numbers is crucial for effective inventory management, but even small mistakes can lead to confusion and inefficiencies. Here are some common pitfalls to watch out for and how to avoid them:
|
Mistake |
Explanation |
How to Avoid It |
|
Using inconsistent formats |
Variations in SKU formats create confusion and make inventory tracking harder. |
Create a standardized format for all SKUs and document it clearly for your team to follow. |
|
Including too much information |
Overloading SKUs with excessive details makes them long and hard to interpret. |
Focus on the most important product attributes and keep SKUs concise. |
|
Using confusing characters |
Characters like slashes (/), spaces, or O vs. 0 can cause misinterpretation or system errors. |
Stick to alphanumeric characters and use simple separators like dashes or underscores if needed. |
|
Not assigning unique SKUs |
Reusing the same SKU for different products or variations leads to inventory discrepancies. |
Ensure every product, including variations, has a unique SKU. |
|
Ignoring scalability |
A non-scalable SKU format won’t accommodate future product expansion. |
Design a scalable SKU format that can handle new products and attributes without major changes. |
|
Embedding store-specific info |
Including store-specific details in SKUs can confuse multi-channel inventory management. |
Use SKUs for product identification only, relying on other tools for store-level inventory details. |
|
Failing to train employees |
Untrained employees may mislabel or misinterpret SKU numbers, leading to errors. |
Train your team on creating, interpreting, and using SKU numbers effectively. |
|
Not integrating with inventory software |
Manual SKU management leads to errors and inefficiencies, especially with a growing inventory. |
Use inventory software to automate SKU tracking, updates, and reporting. |
|
Overcomplicating SKU names for customers |
Complex SKUs visible to customers (on tags or receipts) can confuse and frustrate them. |
Keep SKUs simple and professional while ensuring internal functionality. |
|
Not regularly reviewing and updating SKUs |
An outdated SKU system becomes messy and misaligned with your current inventory. |
Periodically audit your SKUs to ensure consistency, accuracy, and relevance as inventory changes. |
Final Thoughts
SKU numbers may seem like small details in the big picture of running a business, but their value is undeniable. A well-organized SKU system is a key to unlocking efficiency, better decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction.
By taking the time to create a thoughtful, consistent SKU system, you’re setting your business up for success. Whether they help you stay on top of inventory, offer customers a seamless shopping experience, or scale your operations easily, SKUs are the unsung heroes of business management.
Remember, your SKU system grows with your business. A little effort today can save you countless headaches tomorrow and provide the structure you need to thrive. No matter the size of your business — whether you’re just starting or managing a bustling store or e-commerce site — investing in a solid SKU strategy will pay off in efficiency, organization, and, ultimately, success.
FAQ
Q: What is an SKU number?
A: An SKU number (Stock Keeping Unit) is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to a product to help businesses identify, track, and manage inventory.
Q: How many digits is an SKU number?
A: SKU numbers typically range from 8 to 12 characters, but the length can vary depending on the business’s system and needs.
Q: Where can I find an SKU number?
A: SKU numbers are often found on product tags, packaging, or in a business’s inventory management system.
Q: How is an SKU different from a UPC?
A: An SKU is a customizable, business-specific code for internal inventory tracking, while a UPC is a universal, standardized barcode used globally for product identification.