Supply Chain Risks Explained: Challenges, Examples, and Solutions

Imagine your supply chain as a well-oiled machine, keeping your business running smoothly. Now, picture a single faulty gear causing the entire system to grind to a halt.
Whether it’s a supplier delay, a financial setback, or an unexpected global crisis, supply chain risks can disrupt operations and hurt your bottom line.
For small business owners, supply chain risks can be even more damaging because they often operate with fewer resources, smaller supplier networks, and less financial cushioning compared to large corporations.
That’s why it’s crucial to understand and prepare for them.
In this article, we’ll break down the types of risks in supply chain management, discuss some examples, and explore strategies to protect your business from potential disruptions.
What is a Supply Chain?
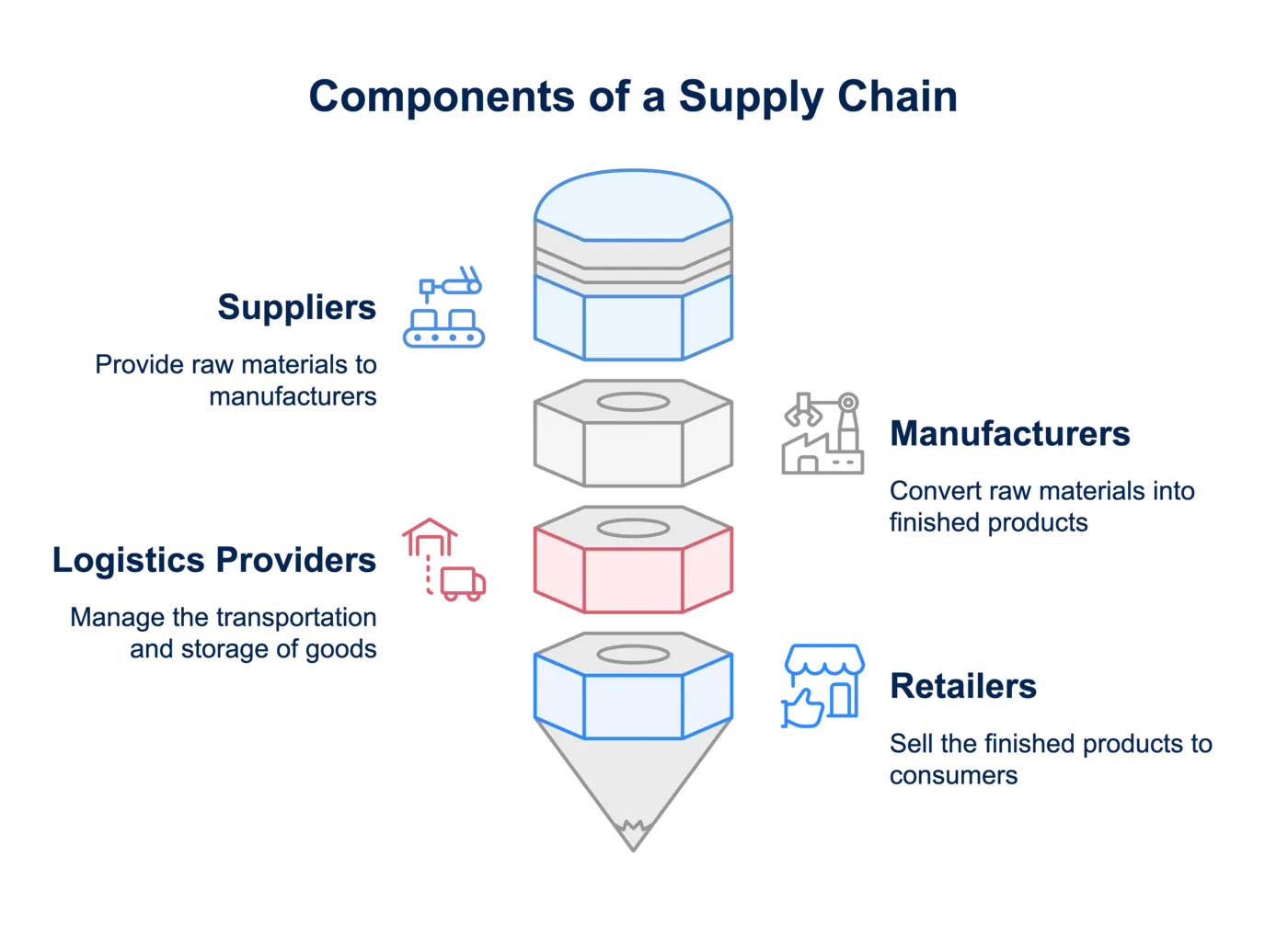
A supply chain is a network of suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and retailers that work together to deliver products or services to customers. It involves sourcing raw materials, production, transportation, and final delivery. Any disruption in this process introduces supply chain risks, which can impact businesses financially and operationally.
For example, a small clothing brand relies on fabric suppliers, manufacturers, and shipping companies. If the supplier faces delays, the entire production is affected, leading to missed deadlines and lost revenue. Understanding the types of risk in supply chain management helps businesses prepare for these challenges and minimize disruptions.
What Are Supply Chain Risks?
Supply chain risks refer to potential disruptions that can affect the flow of goods, services, and finances within a business’s supply chain. These risks can stem from various sources, including economic instability, supplier failures, logistical bottlenecks, and cyber threats.
Small businesses are particularly vulnerable as they often rely on fewer suppliers and have limited financial flexibility.
But don’t fret—there are many strategies you can implement to mitigate these risks, as well as great supply chain management software to help keep things running. We’ll discuss them below.
Supply Chain Risk Management: Importance and Benefits
Effective supply chain risk management helps businesses identify, assess, and mitigate disruptions that could impact operations, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
Given the increasing complexity of global supply chains, businesses — especially small ones — must proactively manage supply chain risks to stay competitive.
Importance of Supply Chain Risk Management
- Minimizes financial risk in supply chain operations: Reduces unexpected costs from supplier failures, inflation, or economic downturns.
- Ensures business continuity: Helps you maintain operations during disruptions like natural disasters or global labor shortages.
- Enhances customer satisfaction: Reliable supply chains prevent stockouts, delays, and quality issues, keeping customers happy.
- Reduces reputational damage: Ethical sourcing and compliance reduce your risk of public backlash and regulatory penalties.
- Increases supply chain resilience: Prepares your business to adapt quickly to changes in demand, supplier performance, or geopolitical risks.
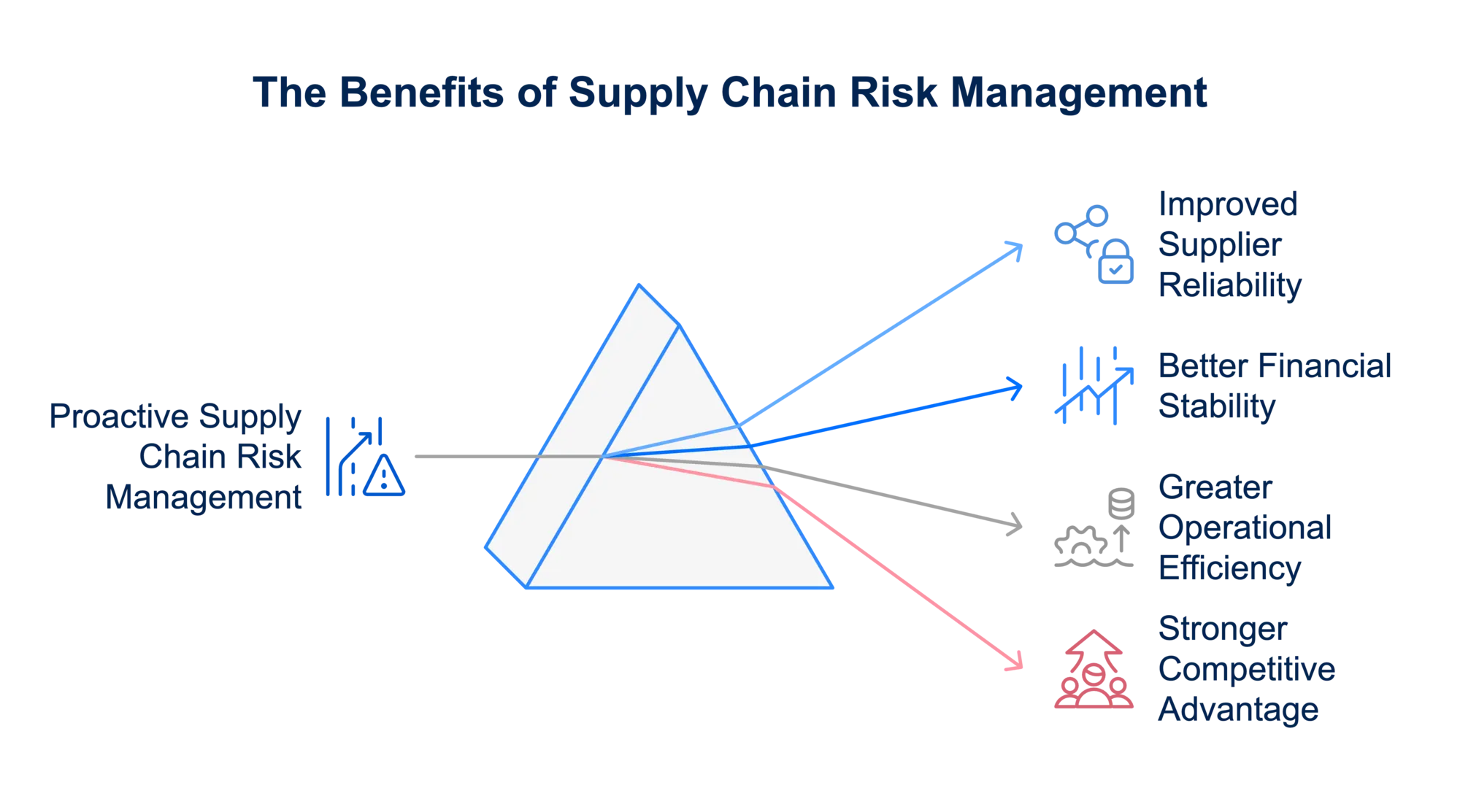
Benefits of Proactive Supply Chain Risk Management
- Improved supplier reliability: Ensures backup suppliers and alternative sourcing strategies.
- Better financial stability: Helps you mitigate financial risk in supply chain disruptions.
- Greater operational efficiency: Reduces delays and optimizes inventory management.
- Stronger competitive advantage: Businesses that handle types of risk in supply chain management effectively can outperform competitors.
By implementing supply chain risk management strategies, you can protect your operations and build long-term resilience.
Supply Chain Management Risks: Examples
Understanding and preparing for supply chain risks enables you to build more resilient operations. By implementing proactive strategies, you can better navigate disruptions and maintain steady growth.
Here are 15 examples of supply chain risks you may encounter:
- Financial Risk in Supply Chains
- Poor Supplier Performance
- Logistics and Transportation Risk
- Demand Fluctuations
- Global Labor Shortage
- Rising Inflation
- Volatile Global Economy
- Geopolitical Risk
- Complex Regulatory Environments
- Cybersecurity Threats
- Natural Disasters and Climate Risk
- Ethical and Social Responsibility Risks
- Quality Control Issues
- Technological Failures
- Global Trade Restrictions
1. Financial Risk in Supply Chain
Financial instability — either within a company, its suppliers, or logistics providers — can cause major disruptions. A key supplier going bankrupt or a sudden increase in material costs can lead to cash flow issues.
This is especially concerning for businesses that may not have backup suppliers or emergency funds to cover unexpected expenses. Managing financial risk in the supply chain involves diversifying suppliers, negotiating favorable payment terms, and maintaining a financial buffer to absorb sudden shocks.
2. Poor Supplier Performance
When suppliers fail to meet quality standards, delivery timelines, or production requirements, businesses face delays and increased costs.
A retailer dependent on an overseas manufacturer might receive late shipments or defective goods, which could affect sales and customer trust. Supply chain risk management requires regular performance reviews and backup supplier agreements to minimize disruption.
3. Logistics and Transportation Risk
Delays, accidents, or strikes in the transportation industry can disrupt the delivery of raw materials or finished products, posing risks to the supply chain.
A trucking strike, for instance, can lead to stock shortages, impacting customer satisfaction and revenue.
Small businesses are particularly affected as they may lack alternative shipping options or the ability to absorb higher transportation costs. Investing in multiple logistics partners and tracking shipments closely can help reduce this risk.

4. Demand Fluctuations
Sudden changes in demand, whether from seasonal trends or market shifts, create risks in supply chain management. Overstocking can lead to financial losses, while understocking can cause missed sales opportunities.
Without sophisticated demand forecasting tools, you may be more vulnerable to these fluctuations. Implementing inventory management software and closely monitoring market trends can help balance supply and demand.
5. Global Labor Shortage
A shortage of skilled labor — from factory workers to truck drivers —- leads to production delays and rising operational costs.
If you depend on third-party manufacturers or logistics providers, you may struggle with fulfillment delays, impacting customer satisfaction. Investing in automation and diversifying supply sources can help mitigate this supply chain risk.
6. Rising Inflation
Inflation drives up costs for raw materials, transportation, and wages, squeezing profit margins. Small businesses often have less negotiating power with suppliers, making them more vulnerable.
In these cases, managing financial risk in supply chain operations includes securing long-term supplier contracts and adjusting pricing strategies to counter inflationary pressures.
7. Volatile Global Economy
Economic downturns, currency fluctuations, and financial crises can disrupt supply chains, reducing consumer spending and increasing supplier instability.
Smaller businesses may struggle to absorb unexpected economic shifts. Maintaining cash reserves and monitoring global economic trends can help mitigate this risk.
8. Geopolitical Risks
Trade wars, military conflicts, and diplomatic tensions can disrupt supply chains by limiting access to essential materials and delivery routes or increasing costs through tariffs.
If your business depends on global suppliers, you must monitor geopolitical developments and establish alternative sourcing strategies to mitigate supply chain risks.
9. Complex Regulatory Environments
Changes in trade laws, import/export restrictions, and compliance regulations create obstacles for businesses relying on international suppliers.
Some businesses may struggle to keep up with evolving regulations, leading to delays or penalties. To manage this supply chain risk, you should work with compliance experts and ensure suppliers adhere to industry standards.
10. Cybersecurity Threats
Supply chains are increasingly digital, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks. A ransomware attack on a supplier’s system could disrupt order processing and delay shipments.
Protecting against this supply chain risk requires implementing strong cybersecurity measures, training employees on data protection, and ensuring that suppliers follow security best practices.
11. Natural Disasters and Climate Risks
Floods, hurricanes, and wildfires can disrupt supply chains by damaging infrastructure, delaying shipments, or affecting raw material availability.
For instance, a small bakery that relies on wheat imports may face shortages due to droughts affecting crop yields.
These types of risks in supply chain management require businesses to develop contingency plans, diversify suppliers, and consider local sourcing options where possible.

12. Ethical and Social Responsibility Risks
Your company’s reputation can be damaged if its supply chain is linked to unethical labor practices, environmental harm, or data breaches. This can often occur in countries where regulations differ from those in the USA.
For example, suppose a supplier in another country is found using child labor or violating environmental laws. In that case, your business may face public backlash, legal penalties, and loss of customer trust — even if you were unaware of the violation.
Conducting due diligence, requiring supplier transparency, and ensuring compliance with ethical standards can help mitigate this risk.
13. Quality Control Issues
Receiving defective or low-quality materials from suppliers can lead to product recalls, customer dissatisfaction, and financial losses.
A small skincare brand, for example, that gets a batch of contaminated ingredients could face reputational damage and regulatory penalties.
To manage this supply chain risk, businesses should implement strict quality checks, conduct supplier audits, and establish clear quality standards.

14. Technological Failures
Many businesses rely on automated systems for inventory management, production, and order processing. If these systems fail — due to software bugs, power outages, or IT disruptions — operations can come to a halt.
Businesses without dedicated IT teams may struggle to resolve such issues quickly. Having backup systems and investing in reliable technology can reduce this risk in supply chain management.
15. Global Trade Restrictions
Sanctions, new tariffs, and import/export bans can disrupt supply chains and increase costs. Businesses relying on foreign suppliers must stay informed about international trade policies and establish contingency plans to minimize disruptions from this supply chain risk.
For example, an American company importing electronic components from China may face sudden tariff increases, raising production costs and forcing them to find alternative suppliers or adjust pricing strategies.
Ways to Overcome Supply Chain Disruptions
Managing supply chain risks requires proactive planning, diversification, and the right technology. Businesses, especially small ones, must adopt strategies to prevent financial losses and operational delays caused by risks in supply chain management.
1. Diversify Suppliers and Logistics Partners
- Work with multiple suppliers to reduce reliance on a single source.
- Establish relationships with regional and local suppliers as backup options.
- Use multiple logistics providers to avoid transportation delays, a key supply chain risk.
2. Improve Demand Forecasting
- Use analytics to anticipate market fluctuations and stock levels.
- Monitor seasonal trends to adjust supply and reduce financial risk in supply chain operations.
- Implement just-in-time inventory management to balance supply and demand.
3. Enhance Supplier Communication and Collaboration
- Maintain real-time updates on order status to prevent poor supplier performance.
- Set performance metrics to minimize delays and types of risk in supply chain management.
- Create backup agreements to ensure continuity during supply chain disruptions.
4. Utilize Supply Chain Management Software
- Automates order tracking, inventory forecasting, and risk assessment.
- Reduces financial risk in the supply chain by optimizing procurement and reducing waste.
- Improves response time to supply chain risks, such as supplier failures or geopolitical disruptions.
Recommended Supply Chain Management Software
- Oracle – Enhance manufacturing with IoT integration
- Precoro – Automated requests, approvals & orders
- BlueYonder – Real-time inventory and order visibility
5. Build Emergency Stock and Financial Reserves
- Maintain safety stock of critical products to mitigate supply chain risk.
- Allocate contingency funds to handle rising costs and supply shortages.
6. Leverage AI-Powered Predictive Analytics
- Use machine learning to analyze historical trends and detect supply chain risks before they escalate.
- Predict demand fluctuations and supplier failures to take preventive actions.
- Anticipate cost increases and adjust budgets accordingly.
Related Articles
7. Automate Supply Chain Risk Assessment
- Utilize supply chain management software to automate risk evaluations and identify weak links.
- Integrate real-time data from multiple sources to assess types of risk in supply chain management proactively.
- Use supplier risk scores to identify potential disruptions before they impact operations.
8. Implement Digital Twins for Scenario Testing
- Create virtual models of the supply chain to simulate disruptions like transportation failures or supplier shutdowns.
- Test different scenarios and refine contingency plans to mitigate supply chain risks.
- Optimize resource allocation by predicting supply chain bottlenecks.
9. Strengthen Cybersecurity Measures
- Protect against cyber risk by encrypting sensitive data and securing digital transactions.
- Ensure suppliers follow cybersecurity best practices to prevent data breaches.
- Implement multi-factor authentication and regular security audits to prevent supply chain disruptions caused by cyberattacks.
10. Adopt Blockchain for Transparency
- Enhance traceability by using blockchain to track supplier transactions and prevent fraud.
- Reduce reputational risk by verifying ethical sourcing and compliance with sustainability mandates.
- Improve supplier accountability by providing a secure, tamper-proof record of the entire supply chain.
11. Enhance Workforce Resilience
- Address global labor shortages by investing in workforce automation and upskilling employees.
- Use AI-driven human resources management tools to optimize scheduling and productivity.
- Leverage LMS systems to establish training programs to ensure employees can adapt to new supply chain technologies.
By leveraging supply chain management software and these strategies, businesses can reduce supply chain risks and build long-term resilience against disruptions.
Key Features of Supply Chain Management Software
Implementing robust supply chain management software is essential for businesses aiming to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and mitigate risks. Below are key features to consider, along with examples of software solutions that offer these functionalities:
- Inventory Management: Efficiently track and manage stock levels to prevent overstocking or stockouts. Example: Netstock.
- Order Processing: Automate order fulfillment processes to reduce errors and expedite delivery. Example: Logiwa.
- Demand Forecasting: Utilize data analytics to predict future product demand, aiding in inventory optimization. Example: Oracle SCM
- Supplier Management: Maintain comprehensive records of supplier performance, contracts, and compliance to ensure reliability. Example: Anvyl
- Logistics and Transportation Management: Plan and monitor the movement of goods to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery. Example: Magaya
- Compliance and Risk Management: Ensure adherence to industry regulations and proactively identify potential supply chain risks. Example: Intelex
- Real-Time Analytics and Reporting: Access up-to-date data to make informed decisions and quickly respond to market changes. Example: E2open
- Financial Management: Oversee budgeting, cost control, and financial planning within the context of the supply chain. Example: Precoro
- Collaboration Tools: Facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among stakeholders across the supply chain. Example: Blue Yonder
- Scalability and Integration: Ensure the software can grow with your business and integrate with existing systems for unified operations. Example: Epicor
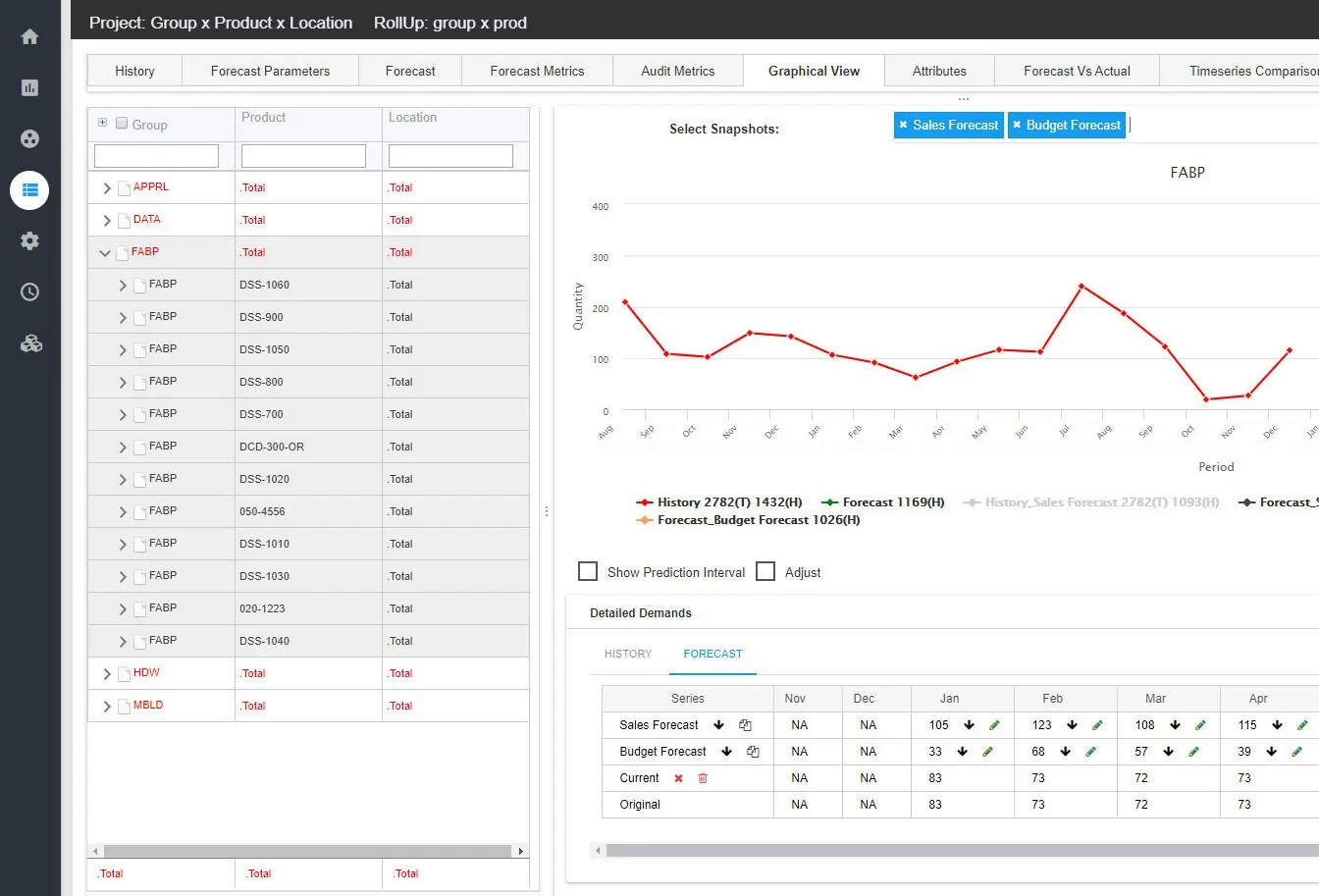
Example: Epicor forecast reporting
By focusing on these features, businesses can enhance their supply chain operations, which can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Final Thoughts
Supply chain disruptions are inevitable, but they don’t have to derail your business. With the right strategies—diversifying suppliers, improving demand planning, and leveraging supply chain management software—you can stay ahead of challenges and keep operations running smoothly. Understanding supply chain risks and proactively managing them helps protect your bottom line, build stronger relationships with suppliers, and improve customer trust.
Small businesses, in particular, can turn potential setbacks into opportunities by staying adaptable and prepared. By taking control of financial risk in supply chain operations and planning for the unexpected, you can create a more resilient and successful business future.
FAQ
Q: What is supply chain risk management (SCRM)?
A: Supply chain risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential disruptions within the supply chain to ensure the continuous flow of goods and services. It addresses risks such as supplier failures, natural disasters, cybersecurity threats, and geopolitical events.
Q: Why is supply chain risk management important for businesses?
A: Effective SCRM helps businesses avoid or minimize disruptions, reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance customer satisfaction. It also ensures compliance with regulations, protects brand reputation, and fosters sustainability.
Q: What are common strategies for mitigating supply chain risks?
A: Common strategies include diversifying suppliers, enhancing supply chain visibility, implementing robust cybersecurity measures, maintaining safety stock, and developing contingency plans. Supply chain management software can also help monitor and respond to potential risks.
Q: How does supply chain risk management differ from supply chain resilience?
A: Risk management focuses on identifying and mitigating potential disruptions, whereas resilience emphasizes the ability of the supply chain to adapt and recover from unforeseen events. Both are critical, but resilience involves strategic planning to turn risks into competitive advantages.