What is Primary Research vs. Secondary Research?

Understanding the different types of market research is crucial for any business looking to make informed decisions and refine strategies. There are four main types of market research that your business needs to leverage: Primary, Secondary, Qualitative, and Quantitative. Each offers unique insights and methods, helping you grasp the nuances of your market, consumers, and competitors.
Whether you’re launching a new product, entering a new market, or tweaking your marketing tactics, this guide will help you choose the right research approach for your needs and understand when to combine them.
What is Market Research?
Market research is the process of gathering and analyzing data about a target market, including consumers, competitors, and market trends. It involves collecting and interpreting data to understand the needs, preferences, and behaviors of a target audience, as well as the competitive landscape and market trends.
As part of your market research strategy, consumer insights research is a crucial process for understanding target markets, involving both quantitative and qualitative aspects. It gathers data on demographics, lifestyles, and consumer behaviors to build comprehensive profiles that inform marketing and product development strategies.
By conducting market research, your business can gain valuable insights that inform its marketing strategies, product development, and innovation efforts. Understanding your target market is crucial for making informed decisions that drive business success.
Importance of Market Research in Business Decision-Making
Market research plays a vital role in business decision-making by providing a foundation for informed choices. Here’s how:
- Customer insights: Helps understand customer needs and preferences through detailed data analysis to boost customer experience.
- Competitive analysis: Analyzes the competitive landscape, identifying strengths and weaknesses.
- Strategy development: Guides effective marketing and sales strategies and product improvements.
- Innovation driver: Fuels innovation by identifying market trends and customer demands.
- Opportunity and risk identification: Such as SWOT analysis, which assists in spotting opportunities and threats, aiding strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Navigational tool: Equips businesses with necessary insights to navigate market complexities and maintain competitive advantage.
- Inventory management: Optimizing inventory levels based on market demand and reducing the risk of overstock or stockouts for better cost management.
The Types of Market Research
There are two main types of research: Primary market research and secondary market research. The type of insights gathered are either qualitative or quantitative insights.
These methodologies utilize various market research methods, such as surveys, focus groups, market reports, and digital analytics. They enable your business to gather essential market research data that guides product methodology and pricing strategies.
For a step-by-step guide on conducting market research, read our article:
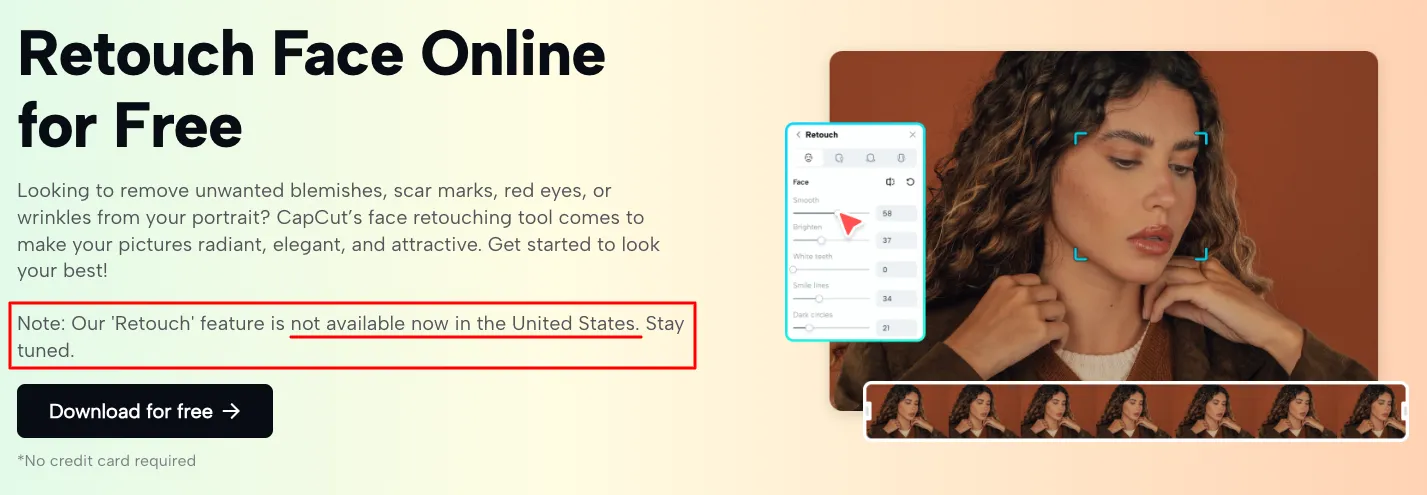
What is Primary Research vs. Secondary Research?
Market research is a crucial activity for gathering insights into market needs and consumer behavior. It encompasses both primary and secondary methods, helping businesses adapt to evolving market dynamics and avoid costly mistakes.
Primary research collects new data through market research surveys and focus groups, providing fresh insights tailored to your specific business needs. Secondary research leverages existing data from global market research reports, website traffic data, and academic studies, offering a broader understanding of market trends.
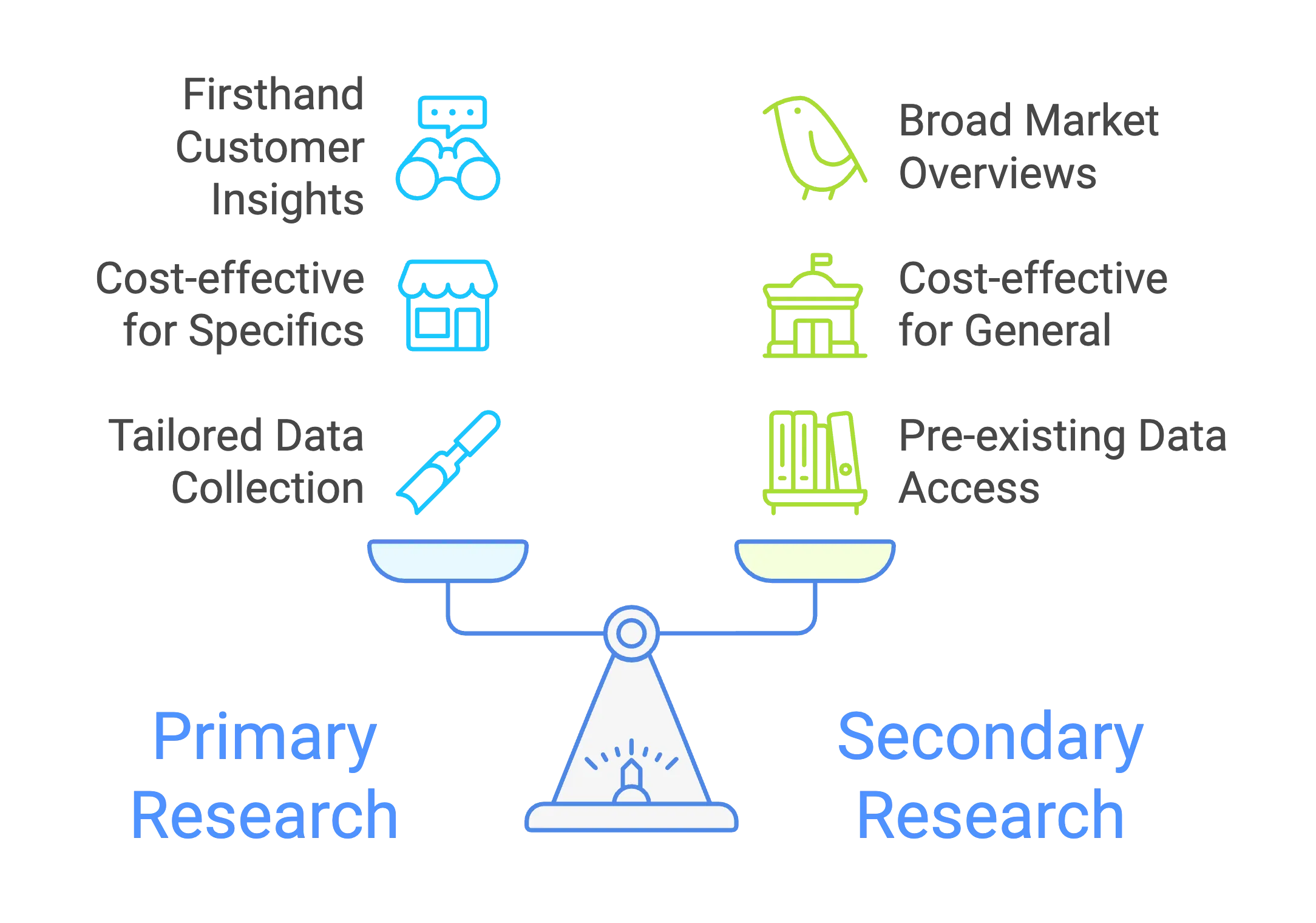
Qualitative Research vs. Quantitative Research
Qualitative market research delves into consumer behavior and motivations through techniques like in-depth interviews and focus groups, capturing consumer insights that help in branding and audience research. Quantitative market research, on the other hand, uses statistical tools to analyze numerical data, providing a solid foundation for data analytics, trend forecasting, and market segmentation.
Together, these methods equip your business with the market research insights needed to perform industry benchmarking, and competitor analysis, and develop sales and marketing strategies.
Digital market research tools enhance the efficiency and scope of data collection, allowing for more precise customer behavior analysis and effective brand positioning.
Whether it’s B2B or consumer market research, the integrated use of these methods and tools helps you optimize business strategies, as well as loyalty and retention programs.
Market Research Methods: Deep Dive
Let’s dive a little deeper into these market research methodologies and discuss some use cases.
1. Primary Market Research
Primary research involves gathering new, original data directly from the source. This method enables businesses to collect highly specific information tailored to their unique needs. Utilizing primary research data is crucial for gathering direct insights from customers, which can inform business decisions and help understand market trends.
Benefits:
Primary research delivers firsthand insights into customer preferences, attitudes, and behaviors. This targeted approach allows businesses to dive deeper into the needs of their target audience to improve their offering and strengthen customer relationships. A company launching a new product can use surveys or focus groups to gauge customer interest and refine features before release.
Example use:
A beverage company might use surveys to determine which flavors customers prefer or use focus groups to test reactions to new product packaging.
Methods:
- Surveys: Collect quantitative or qualitative data by asking customers direct questions.
- Interviews: One-on-one conversations to gain deeper insights into individual opinions or experiences.
- Focus Groups: A small group of participants discussing a product or service to reveal collective attitudes and reactions.
- Observations: Monitoring consumer behavior in natural settings to understand how they interact with a product or service.
Digital tools for primary research:
- Tools like Qualtrics for sophisticated survey designs or FocusVision for detailed focus group analysis — support primary research efforts by providing robust data collection and analysis capabilities.
- Tools like SurveyMonkey for designing and distributing surveys and UserZoom for conducting usability tests and focus groups — provide robust data collection and analysis capabilities.
- CRM software like Salesforce and HubSpot streamline tracking of sales patterns and customer journeys, enhancing data analysis and insight gathering.
Example: Hubspot
2. Secondary Market Research
Secondary market research uses pre-existing data collected by external sources, such as market reports, government publications, or industry analyses.
Benefits: Secondary research is often more cost-effective and faster to obtain than primary research. It’s ideal for gaining a broader understanding of market trends, performing competitor analysis, or exploring general industry insights. Businesses might, for instance, use market reports with industry statistics to assess competitor strategies or identify emerging consumer trends.
Example use: An e-commerce company may use government statistics to analyze demographic data to target its marketing efforts or use competitor analysis to adjust its pricing strategies.
Methods:
- Market reports: Comprehensive industry overviews that highlight market trends and forecasts.
- Academic journals: Research papers and studies that provide deep insights into specific market behaviors or theories.
- Government statistics: Demographic and economic data published by government bodies that offer a broad view of market conditions.
- Competitor websites: Analyze publicly available information from competitors to understand their products, pricing, and marketing strategies.
Digital tools for secondary research:
- Platforms like IBISWorld for accessing detailed market reports and JSTOR for academic articles provide valuable secondary data.
- AI research tools with advanced data processing and consumer insight extraction to find trends on common online subjects.
Recommended AI Tools for Research
Copy.ai – Generates fresh ideas & content with ease
Gemini – AI-powered brainstorming outlines & copy
OpenAI – University-grade AI writing skills
- Website traffic analysis tools like SimilarWeb offer critical insights into competitor traffic sources, visitor engagement, and overall site performance.
- SEO tools and digital market research tools can enhance competitor website analysis and keyword research to understand consumer and market trends.
Recommended SEO Tools for Research
Semrush – Research database with 24B+ keywords
Ahrefs – All-in-one SEO toolset
Yoast – Over 13M happy Yoast SEO users
Example: Ahrefs
When to Use Primary vs. Secondary Research:
Considering the distinct advantages and challenges of each, it’s crucial to determine the right times to utilize primary vs secondary market research.
|
Type of Research |
When to Use |
Examples |
|
Primary Research |
– When specific, original insights are needed. – When exploring customer preferences, attitudes, and behaviors directly. – When validating a concept, product, or feature before launch. |
– Conducting surveys to gather customer feedback on a new product. – Holding focus groups to test customer reactions to a service. – Conducting interviews to explore individual experiences. – Observing customer interactions with a product in real-life scenarios to improve user experience. |
|
Secondary Research |
– When general market trends, competitor analysis, or broad insights are required. – When time or budget constraints make primary research impractical. – When exploring historical data or insights already gathered by others. |
– Reviewing industry market reports to understand market size and emerging trends. – Using government statistics to explore demographic data for new market entry. – Analyzing competitor websites to benchmark pricing and marketing strategies. – Accessing academic journals or publicly available data to gain theoretical or historical perspectives on market behaviors. – Leveraging digital data such as website traffic insights to competing brands to spot leading traffic sources, affiliate partners, and winning marketing campaigns. |
|
Using Both Together |
– When a comprehensive understanding is needed by combining original insights with existing knowledge. |
– Conduct surveys to gather customer-specific feedback, then use market reports to place findings in the context of broader industry trends. – Primary research will be used to identify a customer pain point, and secondary research will be used to explore how competitors address the same issue. |
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
When conducting market research, two types of insights are necessary to gain a comprehensive understanding: Qualitative market research and quantitative market research.
Each approach serves a different purpose, and understanding their differences helps businesses choose the most appropriate method based on their objectives.
|
Aspect |
Qualitative Market Research |
Quantitative Market Research |
|
Objective |
To explore underlying motivations, opinions, and reasons. It helps in understanding why consumers feel or act a certain way. |
It focuses on what consumers think or do in measurable terms, with the goal of quantifying data and generalizing results from a larger sample. |
|
Data Type |
Non-numerical, descriptive data like words, opinions, and themes were collected through open-ended questions. |
Numerical, measurable data such as percentages, averages, and statistics are collected through structured questions. |
|
Methods |
– Focus groups: Small groups discussing topics in-depth – In-depth interviews: One-on-one discussions – Open-ended surveys: Allows for detailed, personalized responses – Observations: Watching how customers behave in real-world settings |
– Structured surveys: Predefined questions with fixed answer choices – Polls: Short questionnaires on specific topics – Questionnaires: Collect data from a large sample with predefined, closed-ended questions – Experiments: Testing hypotheses through controlled variables – Digital data: Seeing the bigger picture of where target audiences spend their time online and which products or marketing campaigns make them click. |
|
Sample Size |
Typically small (5-30 participants), but carefully selected to offer rich insights. |
Large sample sizes (hundreds or thousands) to ensure the data is representative and statistically valid. |
|
Analysis |
Interpretive analysis that identifies patterns, themes, and subjective meanings from data. Often uses tools like content analysis and coding frameworks. |
Statistical analysis uses methods like cross-tabulation, correlation, and regression analysis. Focused on objective measurement and testing hypotheses. |
|
Benefits |
– Deep insights: Uncovers emotional and psychological factors – Flexibility: Questions can evolve during interviews – Rich data: Provides context to understand the “why” behind behaviors and preferences |
– Broader scope: Can generalize results to a larger population – Objective: Data is measurable and quantifiable – Predictive: Can forecast trends and predict future outcomes |
|
Challenges |
– Time-consuming: Data collection and analysis are slower – Subjective: Results can be harder to interpret or generalize – Smaller sample size: May not represent larger market trends |
– Less depth: Provides less understanding of underlying motivations – Rigid: Structured questions limit the depth of responses – Expensive: Requires larger sample sizes and statistical expertise |
|
When to Use It |
– Ideal for early stages of product development or when exploring new markets – Useful for generating ideas, understanding behaviors, and identifying why customers behave a certain way. |
– Best for validating hypotheses, estimating market sizes, or measuring customer satisfaction across a large group. – Ideal for making data-driven decisions that require quantifiable evidence. |
Best Practices for Conducting Market Research
Conducting market research requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the data collected is accurate, reliable, and relevant. Here are some best practices for conducting market research:
Ensuring Data Quality and Accuracy
Ensuring data quality and accuracy is critical in market research. Multiple research methods, such as surveys, focus groups, and interviews, can be used to triangulate data and increase validity.
Additionally, researchers should ensure that the data collection process is well-designed and that the data is collected from a representative sample of the target market.
High-quality data provides a solid foundation for making informed business decisions and developing effective strategies.
Avoiding Biases and Assumptions
Biases and assumptions can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of market research data. Researchers should be aware of their own biases and assumptions and take steps to minimize their impact on the research process.
This can be achieved by using objective language in surveys and interviews and by avoiding leading questions or prompts.
By maintaining neutrality and objectivity, researchers can ensure that the data collected is a true reflection of the target market’s opinions and behaviors.
Using Multiple Research Methods for Triangulation
Using multiple research methods, such as surveys, focus groups, and interviews, can help to increase the validity and reliability of market research data.
This approach, known as triangulation, involves using multiple methods to collect data and then comparing and contrasting the results to identify patterns and themes. By using multiple research methods, researchers can increase confidence in their findings and reduce the risk of biases and assumptions.
Triangulation provides a more comprehensive understanding of the target market, leading to more accurate and actionable insights.
Leveraging Competitive Market Research
Competitive research is an essential component of both primary and secondary research. It helps businesses understand their competitors’ strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Primary competitive research: Through surveys, interviews, or mystery shopping, businesses can gather firsthand insights from customers who use competitors’ products, helping them to identify what works and what doesn’t.
- Secondary competitive research: Analyzing publicly available data — such as financial reports, customer reviews, website traffic insights, and social media trends — enables businesses to benchmark against competitors and find areas for differentiation.
Integrating Market Research Types
Integrating different types of market research — primary, secondary, qualitative, and quantitative—can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the market landscape.
- Primary research might uncover initial consumer reactions and preferences through direct interactions, while secondary research can supplement this with broader industry data and trends.
- Qualitative insights can give depth to the numerical data gathered through quantitative methods, offering a fuller picture of consumer behavior and market dynamics.
This blended approach allows businesses to validate hypotheses with robust data and tailor informed and nuanced strategies.
Integrating the four types of market research can greatly enhance the depth and accuracy of your business insights.
By combining qualitative and quantitative research, businesses can achieve a balanced view that leverages the strengths of each method. For instance, qualitative data from focus groups or interviews can provide detailed consumer perceptions and experiences, revealing the ‘why’ behind behaviors. This can then be quantitatively tested across a broader audience through surveys to validate the prevalence and significance of these insights.
Such an integrated approach enriches the understanding of consumer behavior. It ensures that strategies are both empathetic to customer needs and backed by solid data, leading to more informed decision-making and effective marketing strategies.
Challenges and Solutions
Like any big endeavor, comprehensive market research can have its own set of challenges, which can result in inaccuracies or missed opportunities.
Here are a few difficulties you may encounter and ways to resolve these issues:
|
Challenge |
Solution |
|
Data overload |
Use advanced data analytics tools to manage large datasets. Prioritize data based on research goals. |
|
Biased responses |
Ensure neutrality in questions and use skilled moderators. Triangulate data from multiple sources. |
|
High costs |
Combine primary with secondary research to cut costs. Utilize online tools for cost-effective data collection. |
|
Accessing relevant respondents |
Employ online recruitment tools and social media to find and engage the right participants. |
|
Limited geographic reach |
Use digital market research tools to expand reach globally. Leverage social media and online panels. |
|
Maintaining participant engagement |
Utilize engaging survey techniques and interactive tools. Provide incentives for completion of studies. |
|
Rapid market changes |
Employ real-time data collection and analysis methods. Adapt research strategies quickly to changing conditions. |
|
Integrating diverse data sources |
Implement data integration tools to consolidate and harmonize information from various sources. |
Final Thoughts
Diving into market research can seem like navigating a vast ocean of data, but with the right tools and strategies, it becomes an invaluable compass for any business.
Whether you’re piecing together customer preferences with primary research or shaping your strategies with insights from secondary sources, each step brings you closer to understanding your market landscape.
The goal is to blend these diverse methods to craft a well-rounded view that drives informed decisions. So, go forth with curiosity and the confidence that every piece of data has a story to tell that can propel your business forward.
FAQs
Q: What is the main purpose of market research?
A: Market research helps businesses understand their customers, competitors, and overall market environment. It’s used to make informed decisions and tailor marketing strategies to meet customer needs better.
Q: How often should a business conduct market research?
A: It varies based on goals and industry changes, but regularly updating market research—annually or biannually—helps keep strategies relevant and proactive.
Q: Can small businesses benefit from market research?
A: Absolutely! Even with limited budgets, small businesses can use market research to identify niche market opportunities, understand customer preferences, and compete effectively against larger companies.
Q: What’s the difference between qualitative and quantitative market research?
A: Qualitative research focuses on understanding the reasons and motivations behind behaviors through methods like interviews and focus groups. Quantitative research quantifies data to look at trends and patterns using surveys and statistical analysis.