How HR Can Craft a Change Management Strategy

Change is a natural part of any business, whether it’s driven by new technology, shifting markets, or organizational growth. For HR professionals, managing change means more than updating policies or processes — it’s about supporting employees through transitions that impact their roles and routines. This is where HR change management shines.
By mastering change management in HR, organizations can turn challenges into opportunities. With clear communication, training, and support, HR helps employees embrace change, minimizing disruption and fostering success.
What is Change Management in HR?
At its heart, change management in HR is about preparing, guiding, and aligning employees with the organization’s goals. Whether it’s adopting a hybrid work model, rolling out new policies, or restructuring teams, HR ensures these changes happen smoothly, keeping employees motivated and productive.
Change management focuses on minimizing disruption while maintaining productivity and morale. It ensures that employees, managers, and stakeholders are prepared, supported, and engaged throughout the transition.
The business landscape continually evolves, making adaptability a prized asset. HR’s involvement is pivotal, as it connects the strategic goals of the organization with the people who bring those goals to fruition.
The Role of HR in Change Management
HR plays a pivotal role in change management by aligning organizational goals with the human side of transitions.
From assessing employee readiness to facilitating clear communication, HR ensures the smooth implementation of changes like new policies, technologies, or leadership structures. They provide training, monitor progress, and address resistance to maintain productivity and morale. By fostering collaboration between stakeholders and employees, HR bridges gaps and builds trust.
Additionally, HR ensures compliance with legal standards and tracks the impact of change to refine strategies. This holistic approach empowers organizations to adapt successfully while keeping employees engaged and aligned with business objectives.
Examples of Change Management in HR
Change in organizations comes in many forms — some are subtle, while others create significant shifts in operations and culture. Regardless of scale, these transitions require HR’s guidance to ensure smooth execution and minimal disruption.
Here are some key HR change management examples:
- Leadership transitions: Onboarding or offboarding C-suite executives.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Aligning teams and cultures during transitions.
- Team restructuring: Managing role realignments and new responsibilities.
- Workforce reductions: Handling layoffs with communication and support.
- New technologies: Rolling out and training on new HR systems or tools.
- Flexible work policies: Implementing remote or hybrid work arrangements.
- Regulatory updates: Ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations.
- Talent acquisition: Scaling recruitment or leadership development.
- Workforce challenges: Addressing labor shortages or remote work demands.
- Global expansion: Supporting HR functions in new office openings.
- Diversity initiatives: Building equitable hiring practices and programs.
- Well-being programs: Promoting mental health and employee wellness.

The Importance of Change Management for Business Success
Effective HR change management is critical for navigating transitions and achieving organizational goals. Here’s why change management in HR is essential:
- Minimizes disruption: Helps employees adapt to changes like new policies or technologies without impacting productivity.
- Increases employee buy-in: Clear communication and support foster trust and reduce resistance.
- Aligns people with goals: Ensures employees are prepared to contribute to evolving business objectives.
- Supports innovation: Facilitates adoption of new tools, processes, and strategies.
- Enhances resilience: Builds a culture where employees embrace change and adapt quickly.
- Reduces risk: Ensures compliance with regulations during organizational shifts.
- Improves retention: Prevents turnover by addressing employee concerns during transitions.
By understanding what change management in HR is and applying proven strategies, businesses can overcome hurdles and achieve enduring success.
10 Steps to Craft an Effective Change Management Strategy
Crafting a solid HR change management process is crucial for guiding employees and organizations through transitions successfully. Here are actionable steps to build an effective HR change management strategy, including best practices and tips:
1. Assess Organizational Readiness
Before implementing change, assess how prepared the organization and employees are for the transition. This step identifies potential roadblocks and highlights areas needing support.
- Conduct surveys to gauge employee attitudes toward the change.
- Analyze skills gaps to plan for upskilling and training needs.
- Review historical data to forecast potential impacts.
Tip: Use readiness assessments to identify key influencers who can champion the change.
2. Define Clear Objectives and Scope
Establish the purpose and expected outcomes of the change to align stakeholders and employees.
- Clarify the “why” behind the change and its benefits.
- Set measurable goals and success metrics.
- Identify roles and responsibilities for smooth implementation.
Tip: Use SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals to maintain focus.
3. Build Leadership Support
Leadership buy-in is critical to drive change and influence employee engagement.
- Secure commitment from senior leaders to champion the change.
- Train leaders on how to communicate and model desired behaviors.
- Provide regular updates to keep leadership informed and involved.
Tip: Use leadership as visible sponsors of the change to inspire trust and confidence among employees.
4. Engage Stakeholders Early
Involve key stakeholders at the outset to foster collaboration and alignment.
- Identify all stakeholders, including department heads, managers, and employees.
- Create a cross-functional team to support the change effort.
- Address stakeholder concerns early to avoid resistance.
Tip: Use workshops or focus groups to gather input and build consensus.
5. Develop a Communication Plan
Transparent and consistent communication fosters trust and reduces resistance.
- Outline key messages tailored to different stakeholder groups.
- Use multiple channels (emails, meetings, FAQs) for updates.
- Encourage feedback to address employee concerns.
Tip: Highlight how the change aligns with organizational goals and employee benefits to increase buy-in.
6. Create a Risk Mitigation Plan
Anticipate potential challenges or weak links and develop strategies to address them.
- Identify risks, such as employee resistance or resource constraints.
- Develop contingency plans for critical issues.
- Monitor for emerging risks throughout the change process.
Tip: Regularly review and update the risk plan as the change progresses.
7. Provide Training and Resources
Equip employees with the tools and knowledge they need to succeed in their new roles.
- Offer customized training programs for affected teams.
- Provide user-friendly resources like guides and FAQs.
- Incorporate collaborative tools to streamline the learning process.
Tip: Use technology platforms like Learning Management Systems to support the learning process and track training progress. Then, adapt as needed.
8. Monitor and Adjust
Track the progress of the change and make adjustments to address any challenges.
- Collect employee feedback through surveys and check-ins.
- Use data analytics to measure performance against objectives.
- Identify areas for improvement and act quickly to resolve issues.
Tip: Celebrate small wins through gestures like team lunches, shout-outs in meetings, personalized thank-you notes, or small rewards to maintain momentum and employee morale.
9. Foster a Culture of Change
Encourage a mindset that embraces adaptability and innovation.
- Promote change as a positive opportunity for growth and improvement.
- Recognize and reward employees who actively support the change.
- Integrate change readiness into performance evaluations and onboarding.
Tip: Share success stories of past changes to build confidence and enthusiasm.
10. Sustain the Change
Ensure the change becomes part of the organization’s culture and practices.
- Conduct follow-up training to reinforce new behaviors and skills.
- Establish long-term monitoring systems to measure impact.
- Incorporate the change into policies, workflows, or organizational goals.
Tip: Schedule periodic reviews to ensure the change remains relevant and effective.
5 Popular Change Management Methodologies
To successfully navigate organizational transformation, it’s essential to leverage proven change management methodologies that address both the technical and human aspects of change.
These methodologies each offer unique strategies to navigate organizational change:
- The Prosci and the ADKAR Model focus on individual transitions
- The Kotter’s 8-Step Process and Lewin’s Model emphasize systematic steps for driving transformation
- The McKinsey 7-S Framework ensures structural and strategic alignment
Together, these approaches address diverse organizational needs, helping businesses adopt change effectively and sustainably.
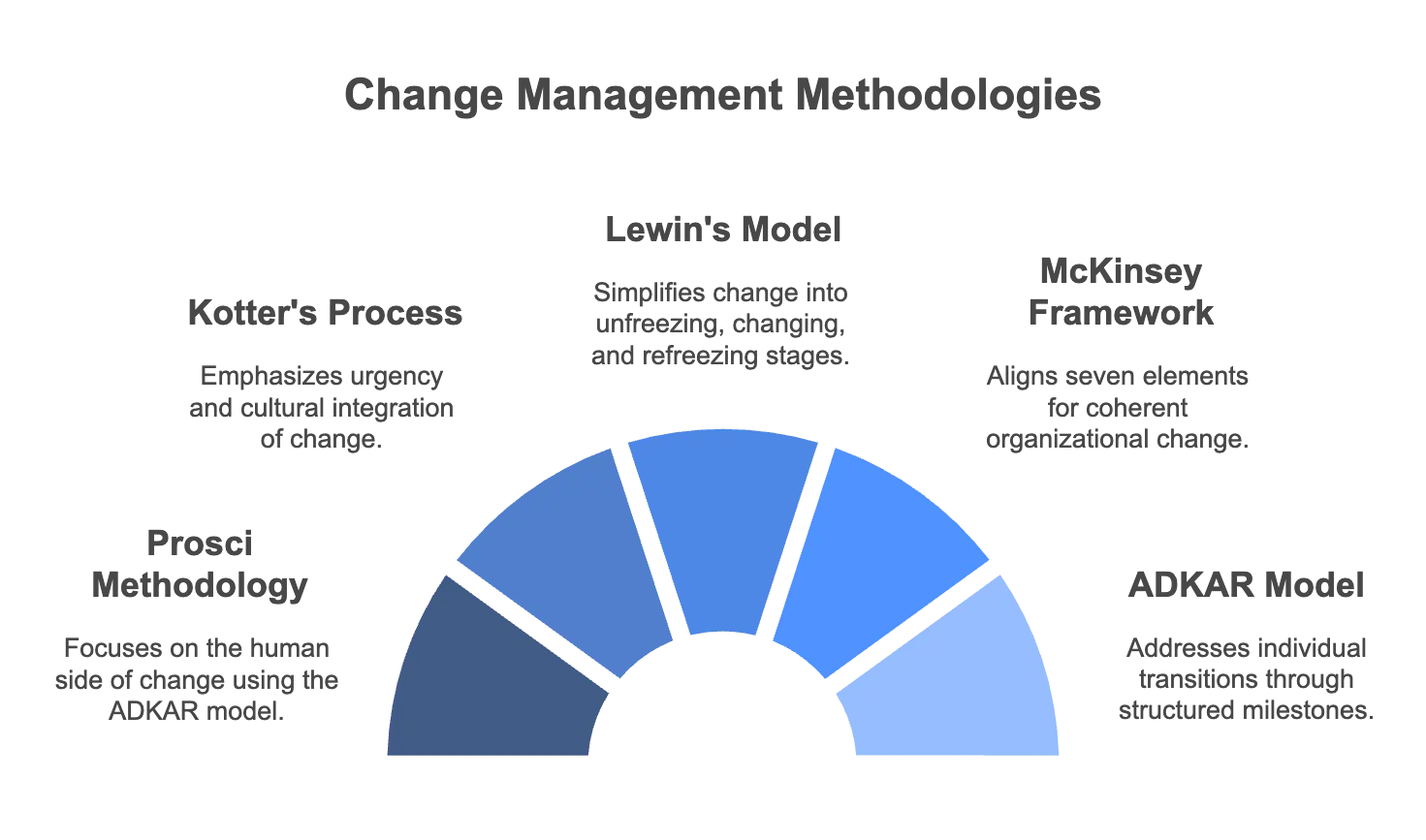
1. Prosci Methodology
The Prosci Methodology centers on the human side of change, integrating individual and organizational strategies for effective transformation.
A key component is the ADKAR Model — Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement — which provides a structured framework to guide individual transitions.
The methodology’s three-phase process ensures that both the technical and people sides of change are addressed, leading to lasting organizational success.
- Prepare: Define the change strategy and secure sponsorship to build a strong foundation.
- Manage: Implement the change plan with clear actions and engage stakeholders effectively.
- Sustain: Reinforce the change through measurement, feedback, and continuous support.
2. ADKAR Model
A core element of the Prosci Methodology, the ADKAR Model focuses on individual transitions through five milestones:
- Awareness: Recognize the need for change and understand its importance.
- Desire: Build motivation and commitment to support the change.
- Knowledge: Acquire the skills and information needed for the transition.
- Ability: Apply the knowledge and skills to implement the change effectively.
- Reinforcement: Sustain the change through ongoing support and recognition.
This model is designed to address personal resistance to change and ensure individuals are prepared, supported, and empowered to adopt new practices.
Its structured approach helps organizations achieve successful and sustainable change by prioritizing the readiness and progress of each person involved.
3. Kotter’s 8-Step Process for Leading Change
John Kotter’s approach emphasizes the importance of creating urgency and building momentum for change. The eight steps include:
- Establish a Sense of Urgency: Highlight the need for immediate action to inspire commitment.
- Form a Guiding Coalition: Assemble a strong team with authority and influence to lead the change.
- Develop a Vision and Strategy: Create a clear and compelling vision with actionable steps.
- Communicate the Vision: Share the vision consistently and effectively to gain widespread buy-in.
- Empower Action: Remove obstacles and provide support to enable progress.
- Generate Short-Term Wins: Identify and celebrate early achievements to build momentum.
- Consolidate Gains: Use successes to drive further change and prevent regression.
- Anchor Changes in Culture: Embed new behaviors and practices into the organization’s culture.
The process culminates in embedding the changes into the organization’s culture to ensure they endure. This methodology highlights employee engagement and maintaining motivation throughout the change journey.
4. Lewin’s 3-Step Change Model
Lewin’s model simplifies change into three clear stages: Unfreeze, Change, and Refreeze.
- The Unfreeze stage involves preparing the organization by challenging existing norms and creating readiness for change.
- The Change stage focuses on implementing new processes or behaviors with clear goals and support.
- The Refreeze stage stabilizes these changes, embedding them into daily operations. In dynamic environments, the Refreeze stage may include maintaining flexibility to adapt to evolving needs.
5. McKinsey 7-S Framework
This framework focuses on the alignment of seven interconnected elements to support organizational change:
- Strategy: Define the long-term plan and actions to achieve organizational goals.
- Structure: Outline the organizational hierarchy and reporting relationships.
- Systems: Assess the processes and tools supporting daily operations.
- Shared Values: Identify the core values and culture that drive the organization.
- Style: Evaluate leadership approach and management practices.
- Staff: Ensure the organization has the right people in the right roles.
- Skills: Focus on the competencies and capabilities required for success.
It is primarily a diagnostic tool that helps organizations identify gaps and ensure coherence during transformation efforts.
By addressing these interdependencies, the McKinsey 7-S Framework is particularly effective for optimizing organizational design and enhancing performance during change initiatives.
Addressing Common Challenges in Change Management
HR professionals play a critical role in navigating the challenges of organizational change. Here’s how to handle some of the most common obstacles:
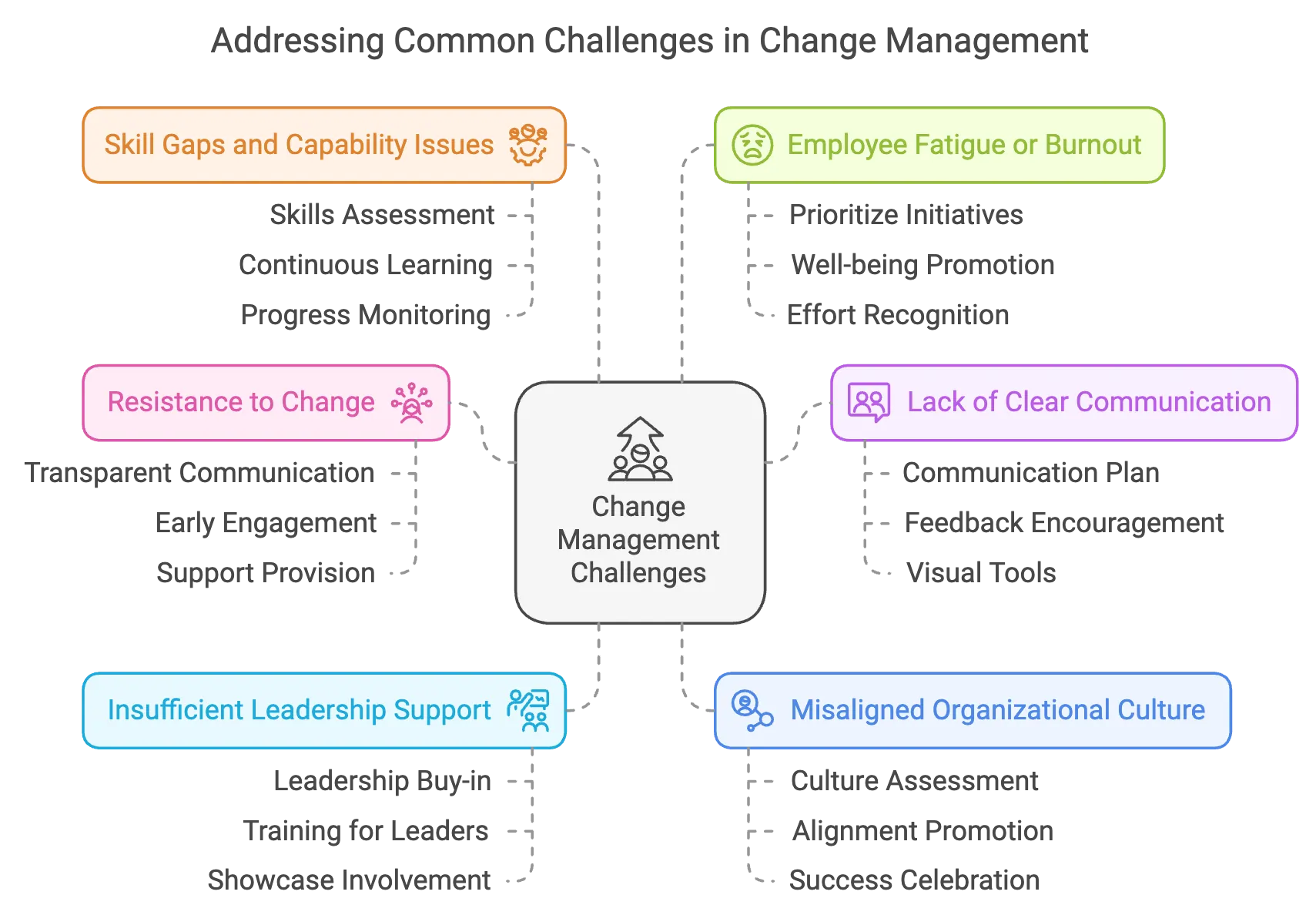
1. Resistance to Change
Challenge: Employees may resist change due to fear of the unknown, job insecurity, or lack of understanding.
HR’s Approach:
- Communicate transparently: Share the vision, goals, and benefits of the change.
- Engage employees early: Involve employees in the planning process to build ownership.
- Provide support: Offer counseling, training, and resources to ease the transition.
2. Lack of Clear Communication
Challenge: Poor communication can lead to confusion and misinformation, undermining change efforts.
HR’s Approach:
- Develop a communication plan: Use multiple channels (emails, meetings, updates) to deliver consistent messaging.
- Encourage feedback: Create opportunities for employees to ask questions and share concerns.
- Use visual tools: Leverage infographics, videos, or dashboards to illustrate complex information.
3. Insufficient Leadership Support
Challenge: Change initiatives can fail if leadership is not fully aligned or visible in their support.
HR’s Approach:
- Secure buy-in early: Work with leadership to articulate their role and responsibilities during the change.
- Provide training: Offer change management training to equip leaders with the tools to guide teams.
- Showcase leadership involvement: Encourage leaders to model the desired behaviors and actively participate in initiatives.
4. Misaligned Organizational Culture
Challenge: Cultural resistance can slow down or derail change.
HR’s Approach:
- Assess current culture: Identify cultural values that may conflict with the change initiative.
- Promote alignment: Highlight how the change aligns with organizational values and goals.
- Celebrate success stories: Share examples of individuals or teams embracing the change.
5. Skill Gaps and Capability Issues
Challenge: Employees may lack the skills needed to adapt to new systems or processes.
HR’s Approach:
- Conduct a skills assessment: Identify gaps and create a training roadmap.
- Provide continuous learning: Offer workshops, e-learning modules, or mentoring opportunities.
- Monitor progress: Track skill development and provide additional support as needed.
6. Employee Fatigue or Burnout
Challenge: Employees can become overwhelmed by the pace or volume of changes.
HR’s Approach:
- Prioritize change initiatives: Avoid overloading employees with multiple changes at once.
- Promote well-being: Offer wellness programs, flexible schedules, and stress management resources.
- Recognize efforts: Celebrate small wins and acknowledge employees’ contributions.
Tools and Resources for HR Change Management
Using the right tools and resources is crucial for an effective HR change management process. These solutions can streamline communication, enhance training, and ensure compliance while driving successful transitions. Here are essential tools tailored for HR professionals:
1. Survey Tools
Survey tools are essential for gauging employee readiness and collecting feedback throughout the HR change management process. Platforms like Zoho Survey allow HR teams to design surveys that assess employee sentiment and identify potential resistance. These tools provide valuable insights that guide decision-making and help tailor strategies for smooth transitions.
2. Project Management Software
Organizing tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities is critical during change management. Project management software such as Monday.com and Wrike are excellent choices for tracking progress and ensuring that all aspects of the transition are coordinated. With features like task assignment, timelines, and collaboration tools, they simplify complex projects and enhance team efficiency.
3. Communication Platforms
Transparent communication fosters trust and minimizes resistance during change. Tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams centralize updates, provide real-time messaging, and facilitate collaboration. These platforms also integrate with other tools to streamline workflows and keep everyone informed.
4. Video and Call Conferencing Systems
Video and call conferencing systems bridge communication gaps, ensuring seamless collaboration during change initiatives. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) platforms like Zoom phone, Vonage, and RingCentral facilitate real-time video, audio, and chat interactions, keeping teams connected regardless of location. With features like screen sharing, breakout rooms, and call recording, these tools support effective discussions, decision-making, and alignment across the organization.
5. Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Training is crucial for equipping employees to adapt to new roles or technologies. LearnUpon LMS and TalentLMS are learning management systems that offer customizable courses and tracking features. These platforms help HR design targeted training programs and monitor progress, ensuring employees are prepared for change.
6. Compliance Management Systems
Ensuring legal and regulatory compliance during organizational changes is vital. Zenefits is a robust platform that manages compliance by tracking employee data, contracts, and legal documentation. It helps HR avoid legal pitfalls and ensures all processes align with regulations.
7. Data Analytics Tools
Tracking the impact of change is critical to measure success and identify areas for improvement. Tools like Zoho Analytics provide in-depth insights into performance metrics, employee feedback, and training effectiveness. This data helps HR teams refine strategies for continuous improvement.
8. HR Software
HR software simplifies the management of employee data, payroll, and benefits. Platforms like BambooHR or Zenefits offer comprehensive features for tracking employee records, automating HR workflows, and enhancing organizational efficiency.
9. Time Tracking Software
Monitoring employee productivity during transitions is essential for staying on track. Tools like TSheets by QuickBooks help HR teams manage work hours, track time allocation and ensure resource efficiency during periods of change.
10. Onboarding Software
Supporting new hires during organizational transitions is key to ensuring quick adaptation. Onboarding platforms like Paycor, BambooHR, and Rippling simplify onboarding with automated workflows, personalized checklists, and centralized documentation.
11. Scheduling Software
Efficient workforce scheduling software is crucial during realignments or structural changes to ensure business continuity. Platforms like Calendly and Schedulicity offer intuitive scheduling features that help manage appointments, avoid conflicts, and keep employees informed.
By leveraging these tools and platforms, HR professionals can enhance every aspect of the change management process, from preparation to implementation, ensuring a smooth and productive transition.
Measuring Success in Change Management
Evaluating the success of a change management process ensures that initiatives meet organizational goals, deliver intended results, and foster continuous improvement.
A structured measurement approach helps HR teams identify what works, address challenges, and refine strategies for future changes. Here are the key methods to measure success:
1. Define Clear Metrics
Establish measurable goals before implementation to track progress and outcomes effectively. Metrics might include:
- Employee engagement levels
- Productivity rates during and after the transition
- Employee retention or turnover rates
- Adoption rates for new tools, technologies, or processes
These metrics ensure alignment with the organization’s objectives and provide clarity on the impact of the change.
2. Monitor Employee Engagement
Employee sentiment serves as a crucial indicator of success. Use surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one feedback sessions to assess:
- How employees feel about the change
- Their understanding of the change’s purpose
- Levels of trust and alignment with leadership
High engagement levels typically reflect successful communication and effective HR support throughout the process.
3. Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs provide insight into how well the change has improved operational and business performance. Examples include:
- Increased efficiency in workflows
- Decreased downtime during transitions
- Revenue or cost savings as a result of the change
Tracking KPIs ensures the organizational value of the change is measurable and supports business goals.
4. Assess Training and Adoption
Effective training and adoption are essential for embedding change. Evaluate:
- Completion rates for training programs
- Employee feedback on training effectiveness
- Real-world application of new tools, systems, or processes
High adoption rates signal that employees are equipped and ready to thrive in the new environment.
5. Solicit Stakeholder Feedback
Gathering feedback from managers, team leaders, and other stakeholders helps:
- Identify alignment between the change and organizational goals
- Address potential barriers or concerns promptly
- Foster collaboration and shared ownership of the change initiative
Open dialogue enhances trust and provides actionable insights for improvement.
6. Measure Long-Term Outcomes
The ultimate success of change management lies in its sustained impact. Periodic reviews can assess:
- The change’s influence on organizational culture
- Employee morale and job satisfaction over time
- Long-term operational and financial performance
Sustained improvements indicate that the change has become a fully integrated part of the organization.
Final Thoughts
Change can be challenging on both professional and personal levels at any stage of your career or business development, but it’s also an opportunity for growth, innovation, and improvement.
By embracing a well-structured HR change management process, organizations can navigate transitions with confidence, keeping employees engaged and aligned with business goals.
HR’s role in change management is essential — it bridges the gap between strategic objectives and the people who make them a reality. With the right tools, clear communication, and measurable goals, you can ensure smooth transitions that drive lasting success.
Whether implementing new policies, adopting technologies, or reshaping your workplace culture, each step forward is an investment in your organization’s future.
Change is not just about processes or outcomes — it’s about people. Empowering employees to adapt, thrive, and embrace new challenges creates a resilient and forward-thinking workplace. By learning from each transition, you’ll not only manage change but turn it into a competitive advantage.
The journey might not always be easy, but with preparation and collaboration, the results are worth it. Embrace change with confidence, and watch your organization — and your people — flourish.
FAQ
Q: What is HR’s role in change management?
A: HR guides employees through transitions, ensuring they are supported, trained, and aligned with organizational goals. HR also facilitates communication, monitors progress, and addresses resistance to ensure smooth implementation.
Q: What are common examples of change management in HR?
A: Examples include implementing flexible work policies, onboarding new leaders, rolling out new technologies, managing mergers, and adapting to regulatory changes.
Q: How can organizations measure the success of change management?
A: Success can be measured through employee engagement, adoption rates, key performance indicators (KPIs), stakeholder feedback, and long-term cultural and operational outcomes.
Q: What tools are essential for HR change management?
A: Tools like project management platforms, learning management systems, survey tools, and communication platforms streamline processes, enhance training, and ensure effective coordination during change initiatives.




